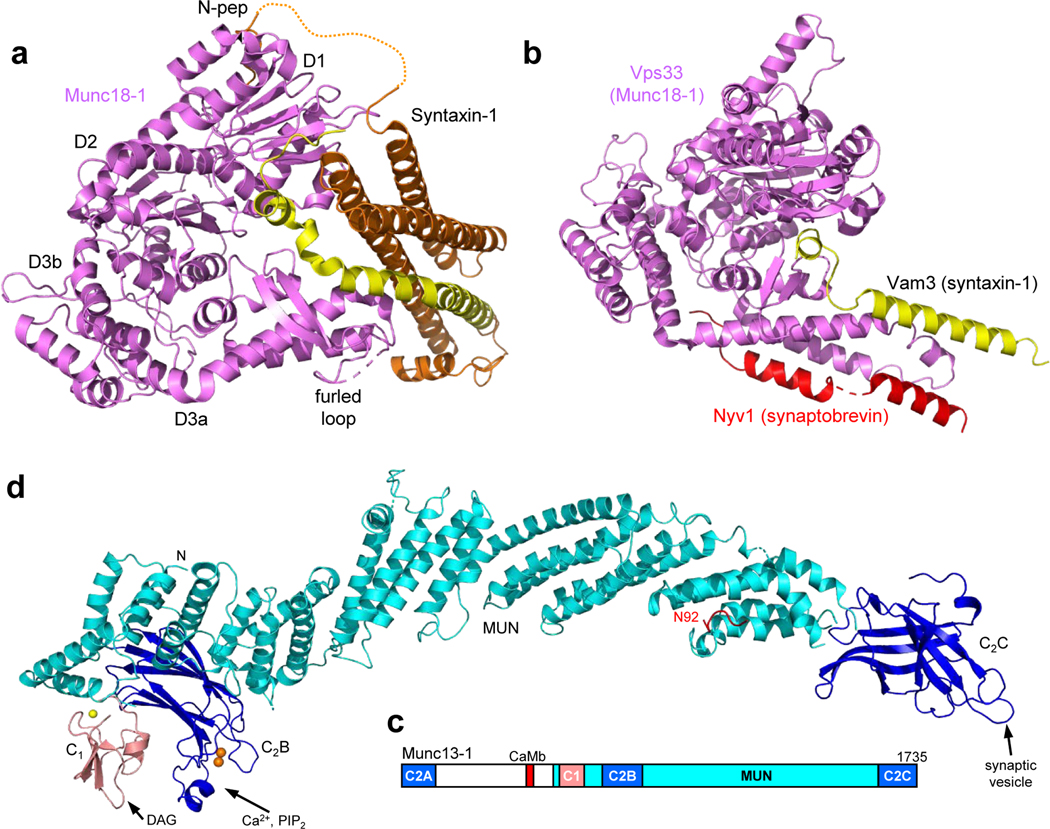
Figure 5.
Structures of the SNARE complex assembly machinery. (a) Ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of Munc18–1 (violet) bound to closed syntaxin-1 (SNARE motif in yellow, N-terminal region in orange) (102) (PDB ID 3C98). The positions of the Munc18–1 domains (D1, D2, D3a and D3b), of the furled loop that covers the synaptobrevin binding site and of the syntaxin-1 N-peptide (N-pep) are indicated. (b) Superposition of crystal structures of the Munc18–1 homologue Vps33 (violet) bound to the SNARE motif of the syntaxin-1 homologue Vam3 (yellow) or the SNARE motif of the synaptobrevin homologue Nyv1 (red) (7) (PDB IDs 5BV0 and 5BUZ, respectively). (c) Domain diagram of Munc13–1. CaMb = calmodulin-binding region. (d) Model of the structure of a fragment spanning the C1 (salmon), C2B (blue) and MUN (cyan) domains of Munc13–1 built from the crystal structure of this fragment (177) and completing the Ca2+-binding region of the C2B domain with the crystal structure of this domain bound to Ca2+ (137) (PDB IDs 5UE8 and 3KWU, respectively). Zinc ions are shown as yellow spheres and Ca2+ ions as orange spheres. N indicates the N-terminus of the fragment, where the Munc13–1 N-terminal region should emerge. A homology model of the Munc13–1 C2C domain (blue) (116) is shown at its expected position at the C-terminus of the MUN domain. The DAG-binding site of the C1 domain, the Ca2+/PIP2-binding site of the C2B domain and the membrane-binding site of the C2C domain, predicted to bind to synaptic vesicles, are indicated. A peptide corresponding to the juxtamembrane region of synaptobrevin is shown in red in the position observed in the crystal structure of this peptide bound to the Munc13–1 MUN domain (163) (PDB ID 6A30). Note that the position of residue 92, which is close to the TM region, is far from the expected membrane-binding region of the C2C domain.