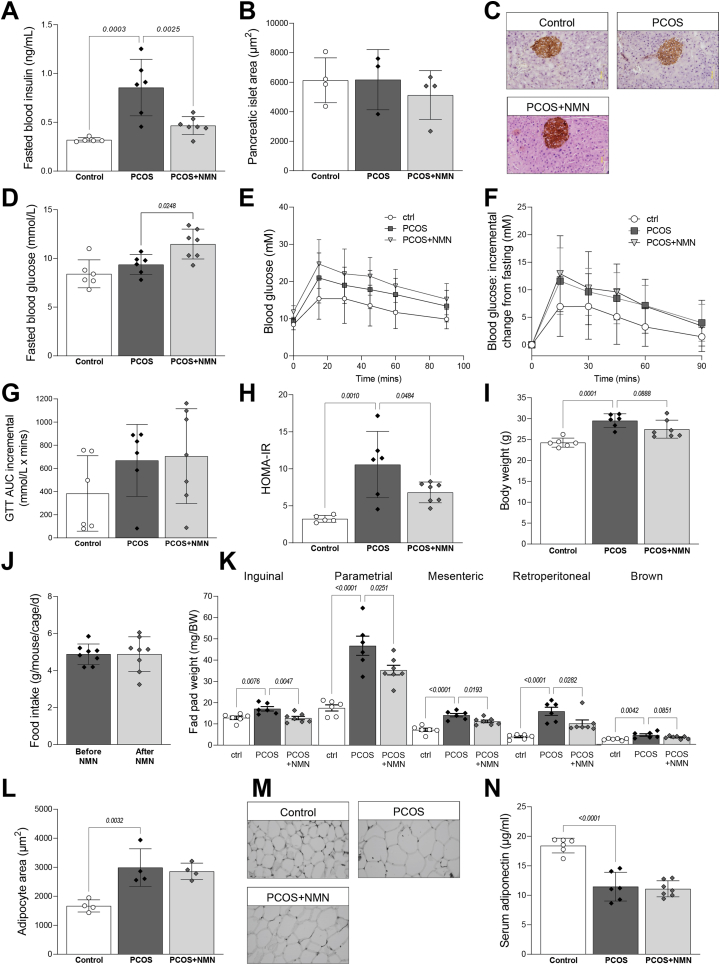
Figure 3.
NMN ameliorates DHT-induced hyperinuslinaemia and obesity.A. Fasting blood insulin levels are increased with DHT treatment and reduced by NMN co-treatment, despite no change in B pancreatic islet area, as assessed by immunohistochemistry, with C representative images shown. D, Fasting blood glucose levels were obtained during glucose tolerance test (GTT), with E incremental area under the curve (iAUC) of GTTs shown. These fasting values were used to calculate F, homeostatic measure of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), showing a significant increase in HOMA-IR in PCOS mice, but a partial amelioration in PCOS + NMN females. DHT treatment increased G body weight, with no impact of NMN treatment on H food intake in PCOS + NMN mice before and after treatment. PCOS mice were obese, with I increased fat pad weights in inguinal, parametrial, mesenteric, retroperitoneal and brown fat-pad weights, however these were reduced in animals co-treated with NMN. J, Histomorphometric assessment of adipocyte diameter in parametrial fat pads, with K, representative histology shown. Increased adipocyte dimeter was matched by F decreased serum levels of adiponectin. n = 6–7 per experimental group and data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Analysed by one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Dunnett's multiple comparison test, p-value results as indicated on graphs. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)