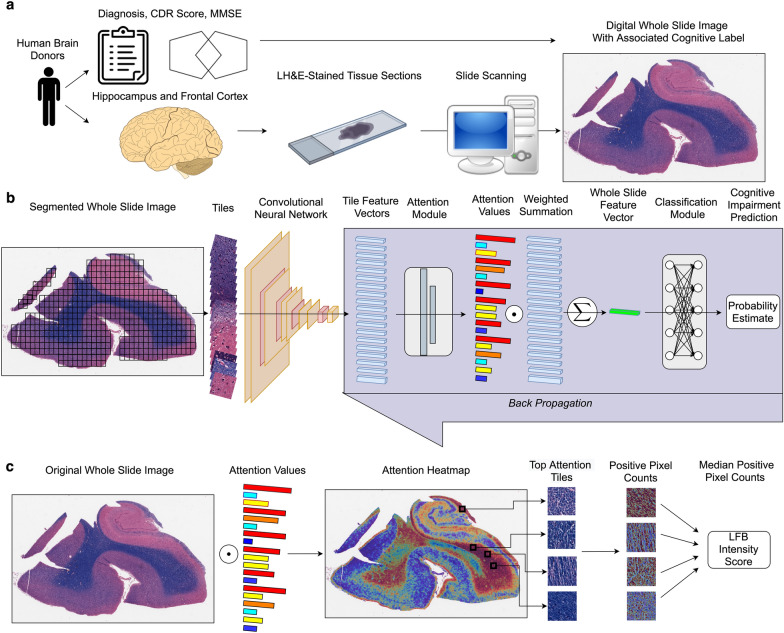
Fig. 1.
Workflow for performing weakly supervised deep learning of age-related cognitive impairment. a: Generation of digital neuropathology whole slide images (WSI) with associated cognitive labels. Human brain sections were stained with Luxol fast blue (LFB) and counterstained with hematoxylin & eosin (LH&E). Cognitive labels were generated based on clinical diagnosis, clinical dementia rating (CDR) scores, and/or mini-mental state exam (MMSE) scores. b: WSI were segmented into tiles and passed through a convolutional neural network for feature extraction. The resulting tile-level feature vectors were passed through an attention network. Each feature vector was multiplied by its associated attention score and a weighted summation operation was performed to create slide-level feature vectors. The slide-level feature vectors were then passed through a classification network. The attention and classification networks were trained via backpropagation. c For interpretation analysis, attention heatmaps were created by mapping the attention scores at their associated tile locations in the original WSI. Among the top attention tiles, a dark blue hue range associated with LFB staining was counted and quantified to calculate a slide-level median staining intensity value