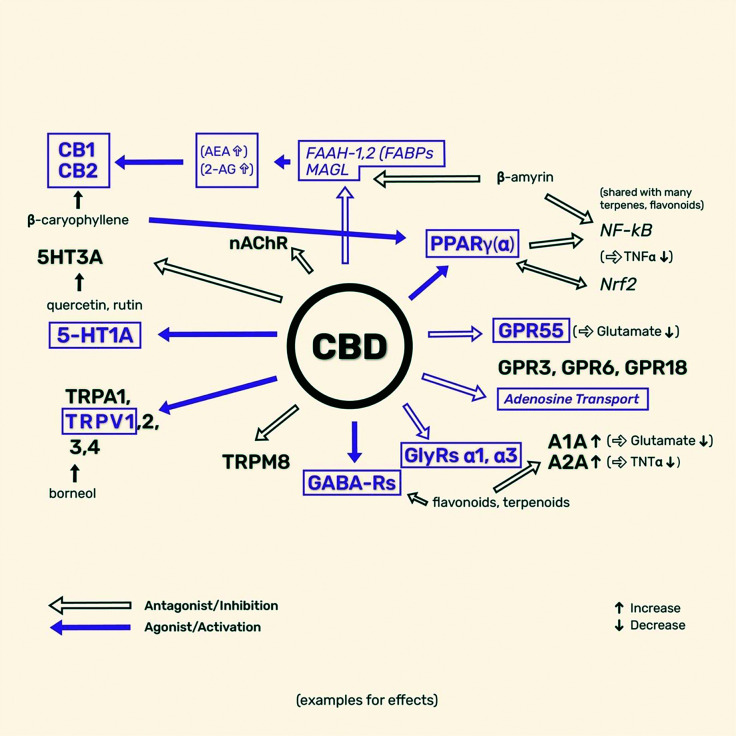
Figure 1.
Examples of the interaction of cannabidiol (CBD) and non-cannabinoids in hemp with the endocannabinoid system. Highlighting in purple some of the interactions with anxiogenic pathways.
A1A, adenosine receptor 1A; AEA, anandamide; 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; CB, cannabinoid receptor; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; FABP, fatty acid-binding protein; GABA-Rs, gamma aminobutyric acid receptors; GlyRs, glycine receptors; GPR, G protein-coupled receptor; GPR55, G protein-coupled receptor 55 (orphan receptor); 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; nAChR, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; NF-kB, nuclear factor-kB; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor-α; TRP, transient receptor potential.
Adapted from ref.21
*As compounded drugs are not patented, ‘Botican’ refers to the trademark brand under which these particular compounded drugs are sold in Mexico.