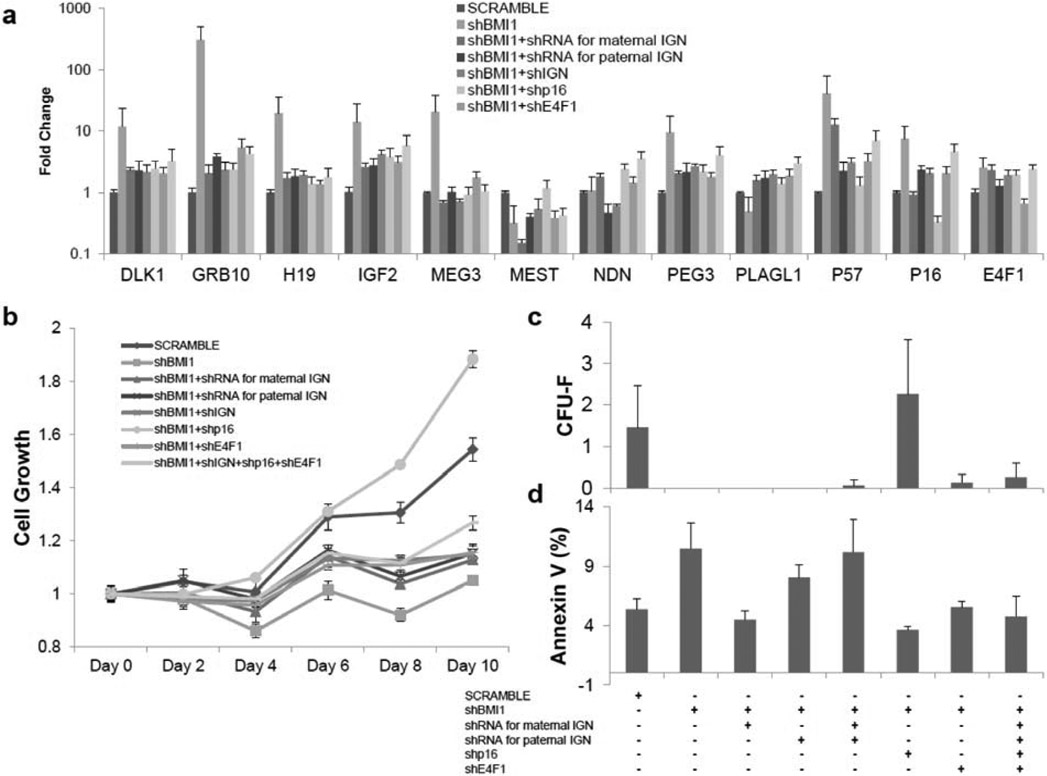
Fig. (2). shRNAs for p16 partially rescues the proliferative defect of BMI1 knockdown MSCs.
(a) mRNA expression of shRNAs for Imprinted Gene Network (IGN), p16 cell-cycle dependent kinases inhibitors and E4F1 in shBMI1 MSCs. Samples were isolated 72 hours including 48 hours of 5 μg/ml puromycin selection after transduction of lentiviral vectors and determined by qRT-PCR, normalized as in Fig 1b. pLKO.1-scramble was used as a vector control (SCRAMBLE). shBMI1; shRNAs for BMI1. shRNA for maternal IGN; p57, GRB10, MEG3 and H19. shRNA for paternal IGN, DLK1, IGF2, MEST, NDN, PEG3 and PLAGL1. shp16; shRNA for p16. shE4F1; shRNA for E4F1. n=3. (b) MTT cell growth assay shows cell proliferation defect in BMI1 knockdown MSCs were rescued by p16 knockdown. Normalization as in Fig 1e. P-values were calculated based on shBMI1 (see supplementary Table 2). n=3. (c) Colony-forming unit-fibroblast assay following knockdown of IGN, p16 and E4F1 shows p16 knockdown overcome growth defect by shBMI1. n=3. (d) Increased apoptosis on shBMI1 MSCs was observed. n=3. *: P0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001, ****: P<0.0005. Data shown as mean ± SEM. See also supplementary Fig. (2).