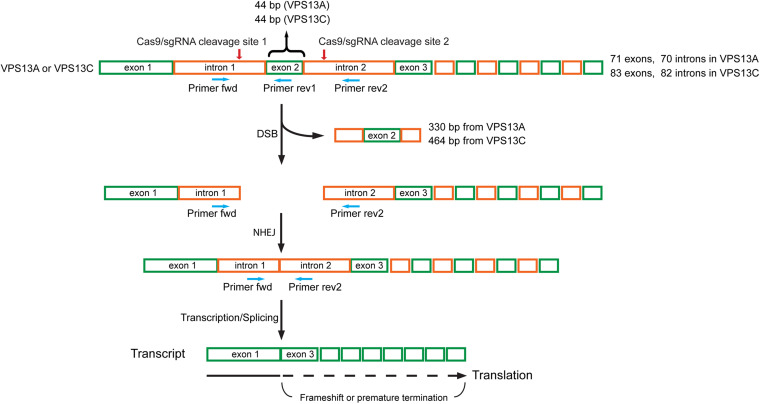
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the strategy used to knock-out VPS13A and VPS13C using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Two sgRNAs were designed to delete exon 2 of human VPS13A or VPS13C. Exon 2 in the VPS13A and VPS13C genes is 44 bp in length. One sgRNA targeted intron 1 on the 5′ side of exon 2, the other targeted intron 2 on the 3′ side of exon 2. Cas9/sgRNAs create two double-stranded breaks (DSBs) that excise the exon 2 containing DNA fragment, 330 bp from VPS13A and 464 bp from VPS13C. Cells repair DSBs via non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) mediated re-ligation of broken DNA ends, but exon 2 was missing in the repaired VPS13A and VPS13C genes and their transcripts. Since the size of exon 2 is 44 bp, the transcript contains frameshift mutations downstream of exon 1, leading to the incorporation of incorrect amino acids in the proteins or premature termination during translation. The primer pair of Primer-fwd (binds to intron 1) and Primer-rev1 (binds to exon 2) was used to detect the deletion of exon 2, and Primer-fwd (binds to intron 1) and Primer-rev2 (binds to intron 2) was used to detect the occurrence of NHEJ between intron 1 and intron 2. Green boxes indicate exons, and orange boxes indicate introns. Red arrows point to the Cas9/sgRNA cleavage site. Blue arrows indicate primers for PCR-based validation.