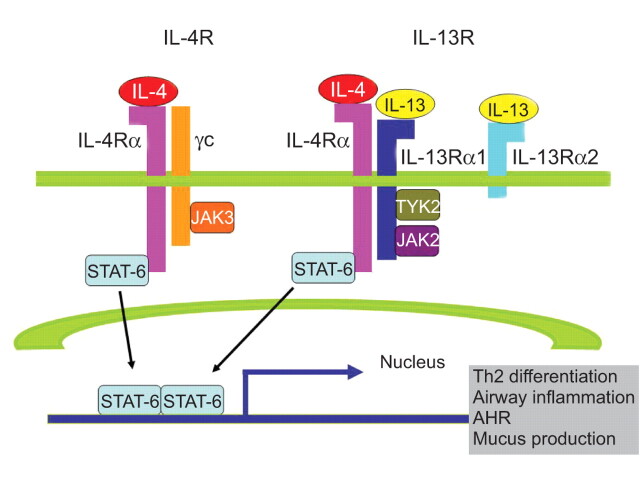
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of the interleukin (IL)-4/IL-13/signal transducer and activator of transcription factor (STAT)-6 signalling pathways [25]. Both IL-4 and IL-13 signal via the IL-4Rα, a component of the type I (IL-4Rα and γc) and type II receptors (IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα1). IL-4 signals via both type I and II receptor pathways, whereas IL-13 signals only via the type II IL-4R. IL-13 also binds to the IL-13Rα2 chain, which does not contain a transmembrane-signalling domain and is thought to act as a decoy receptor. γc activates janus kinase (JAK)3, whereas IL-13Rα1 activates tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) and JAK2. Activated JAKs then phosphorylate STAT-6. Phosphorylated STAT-6 dimerises, migrates to the nucleus, and binds to the promoters of the IL-4 and IL-13 responsive genes, such as those associated with T-helper type 2 (Th2) cell differentiation, airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and mucus production.