Figure 1:
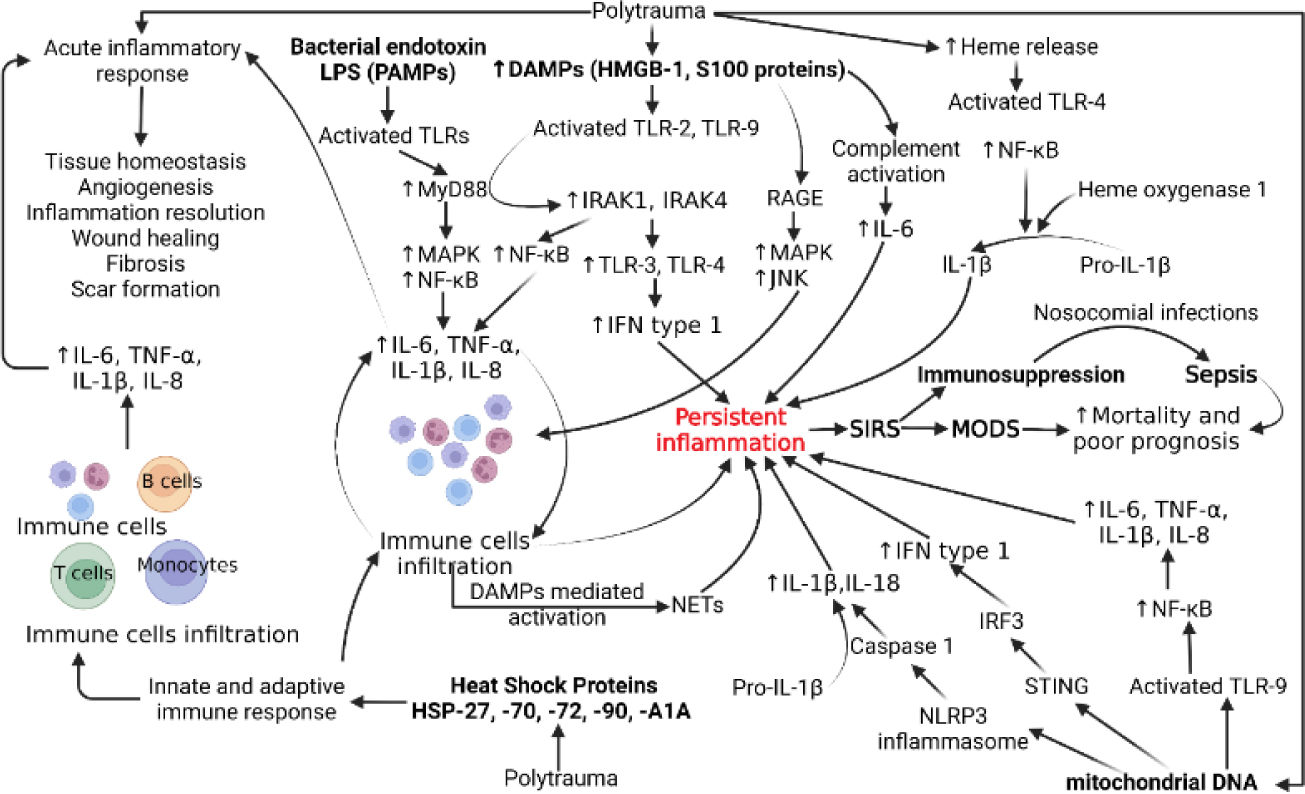
Molecular pathogenesis of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) after polytrauma. Abbreviations: Interleukins (IL), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, damage-associated molecular proteins (DAMPs), pathogen-associated molecular proteins (PAMPs), toll-like receptors (TLRs), receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), high mobility group box protein (HMGB)-1, nuclear factor kappa beta (NF-κB), myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs-JNK, ERK, and p38), interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), interferon (IFN), heat shock proteins (HSPs), neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3), IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), and stimulator of interferon genes (STING).
