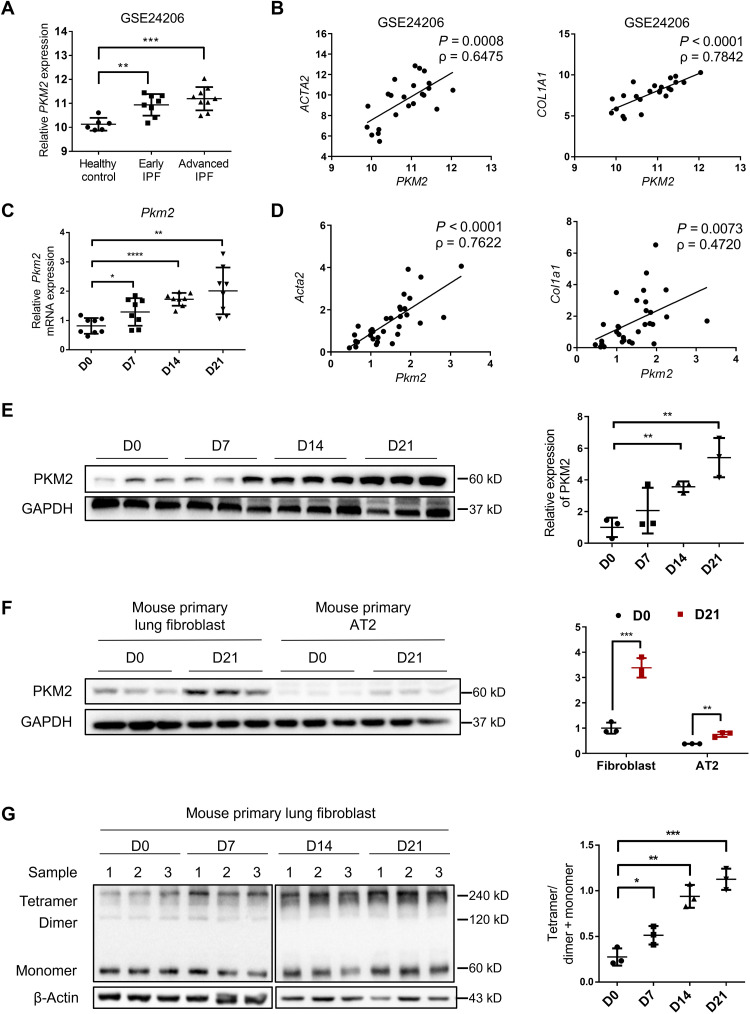
Fig. 1. Increase in PKM2 in patients with IPF and mouse model of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
(A) PKM2 expression in IPF lung tissues in a published GEO dataset of IPF lungs. Microarray analysis of PKM2 mRNA in lung samples of patients with early IPF (n = 8) and patients with advanced IPF (n = 9) compared with healthy controls (n = 6) (B) and the correlation between PKM2 mRNA expressions and those of ACTA2 and COL1A1 in lung tissues. The correlation coefficient (ρ) and the two-tailed significance are shown. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of Pkm2 mRNA expression in the lung tissues of mice following BLM induction (D) and the correlation between Pkm2 mRNA expressions and those of Acta2 and Col1a1 in the same lung tissues (n = 8 per group). Gapdh mRNA levels were used as an internal normalization control. (E) Representative results (n = 3 of Western blot with n = 10 mice per group) for Western blot analysis of PKM2 in the lung tissues of mice. (F) Representative results (n = 3 of Western blot with n = 8 mice per group) of PKM2 in primary lung fibroblasts and AT2 cells isolated from mice following BLM induction. (G) Representative results (n = 3 of Western blot with n = 8 mice per group) of PKM2 in the cross-linked primary lung fibroblasts. Data are represented as the means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, Student’s t test.