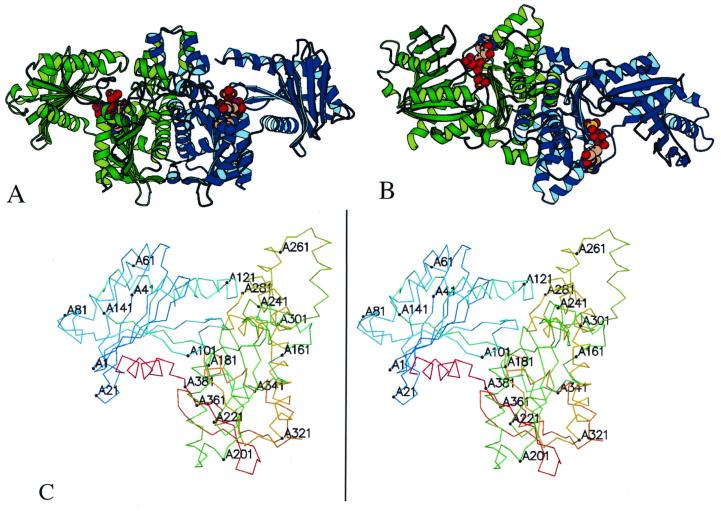
FIG. 1.
Structure of acetate kinase. The structure of the acetate kinase dimer (A) and a view with a 90° rotation around a horizontal axis (B) are shown. The two monomers of the dimer are shown in green and blue. The C-terminal domains, at the center, form the dimer interface. The ADP and sulfate molecules in the active site (between the N and C domains) are shown in space-filling models. The structure contains 801 of the 816 residues in the dimer, with the missing residues located at solvent-exposed regions following the C-terminal helix. (C) Stereoview of monomer A of acetate kinase, numbered every 20 residues.