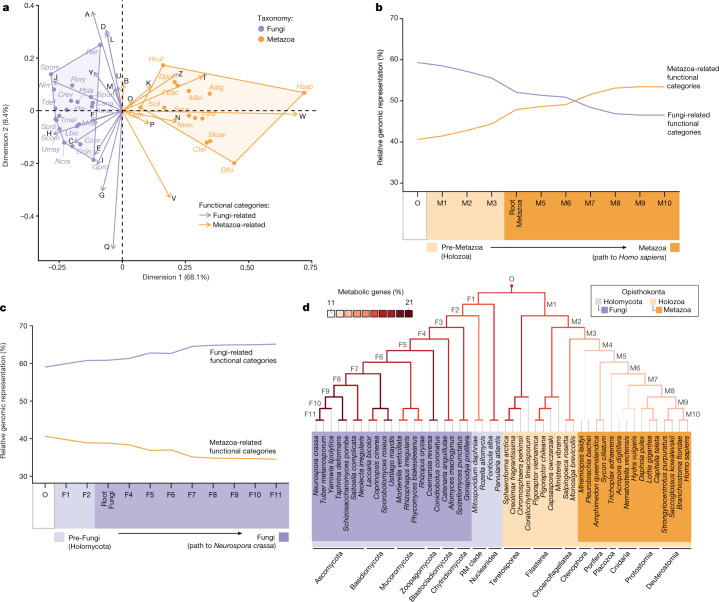
Fig. 2. Gradual compositional change at the gene function level predated the origin of Metazoa and Fungi.
a, Correspondence analysis on the functional category compositions of modern metazoan and fungal gene contents (see species names in Supplementary Table 4). Amphimedon queenslandica was excluded because its outlier behaviour impairs proper data visualization (Extended Data Fig. 6a). Metazoa and Fungi cluster separately in dimension 1, the axis concentrating the largest fraction of variability (68.1%). Functional categories were grouped as Fungi-related or Metazoa-related from their contribution to dimension 1. b,c, Evolution of the functional category compositions in the ancestral paths leading to the species that got the highest scores by the machine learning classifiers that were trained to detect functional category compositions characteristic of Metazoa (b) and Fungi (c) (Supplementary Table 5). See the functional category composition of each ancestral node in Fig. 1d. d, Evolution of metabolic genomic representation in Opisthokonta, measured as the percentage of gene content represented by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Orthology Groups related to metabolism (Supplementary Table 3). Fungi have a larger fraction of their gene content involved in metabolism.