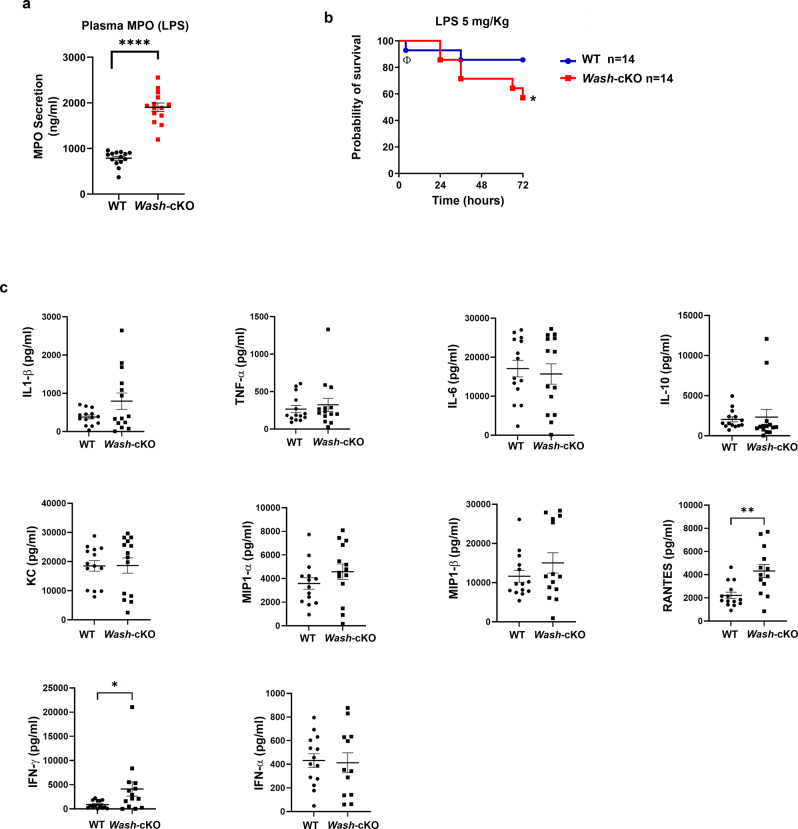
Fig. 8. Increased neutrophil secretion and decreased survival in Wash-deficiency in a model of endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation.
Wild-type (WT) and Wash-cKO mice were challenged with a single intraperitoneal injection of LPS (5 mg/Kg) (E. coli 0111:B4, Enzo). Blood samples were collected at 4 h after injection and mice were subsequently monitored for sickness and survival. a Blood samples from wild-type and Wash-cKO mice were spun down, and plasma was collected and analyzed for the presence of myeloperoxidase (MPO) by ELISA. A total of 14 mice for each group were analyzed in two independent experiments. Mean ± SEM. ****p < 0.0001, Two-tailed Student’s t-test. b Kaplan-Meier survival plots for wild-type (WT), and Wash-cKO mice after challenge with a single intraperitoneal injection of LPS (5 mg/kg). Survival curves were generated from two independent experiments with a total of 14 mice in each group. The early deceased WT mouse, Φ, denotes a statistical outlier (Grubb’s, alpha = 0.05). The difference in survival between the wild-type and Wash-cKO mice was significant by the log-rank test (Mantel-Cox) (*p = 0.0404). c Inflammatory cytokines in plasma of WT and Wash-cKO mice after LPS challenge (4 hours). Each symbol represents one mouse from 2 independent experiments. n = 14 independent mice. IL1β, TNFα, IL6, IL10, KC, MIP1α and MIP1β, IFNα, not significant. Rantes, **p = 0.0022; IFNγ *p = 0.0367, Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. All data in c is represented as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.