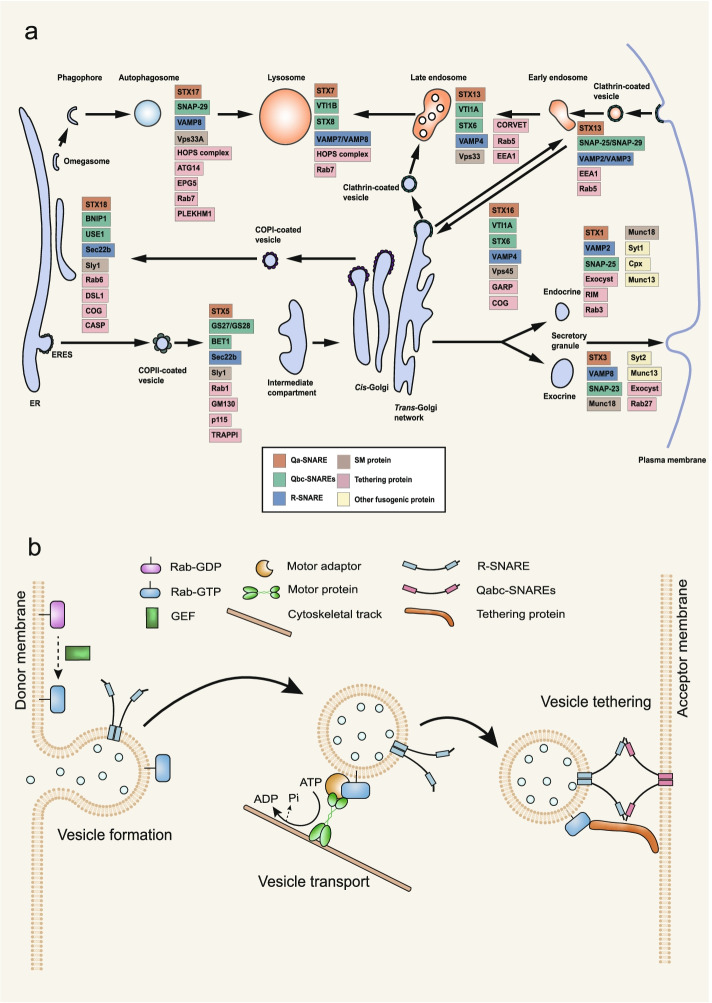
Fig. 2.
Intracellular vesicle trafficking pathways. a The SNAREs, SM proteins, tethering proteins and other fusogenic proteins in intracellular vesicle trafficking pathways. In mammalian cells, intracellular vesicle trafficking includes the ER-to-Golgi transport, the retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport, the TGN transport, the endocytic pathway, the membrane trafficking in autophagy and others. Different SNAREs and fusogenic proteins are assigned to different vesicle trafficking pathways. (Red, Qa-SNARE family; Light green, Qbc-SNARE family; Blue, R-SNARE family; Brown, SM protein; Pink, Tethering protein; Yellow, other fusogenic protein). Vps45, Vacuolar protein sorting 45 homolog; GARP, Golgi-associated retrograde protein. b The working model of vesicle transport and tethering. Rab GTPases mediates vesicle transport along the cytoskeleton tracks (actin filaments or microtubules) by indirectly binding via motor adaptors or directly binding to motor proteins. After cargo containing vesicles being loaded, motor proteins drive vesicles moving along cytoskeleton tracks to the destination by hydrolysis of ATP. Afterwards, GTP-bound Rab recruits tethering proteins to dock vesicles with the acceptor membrane. The copyright permission of panels a and b are from [3, 78]