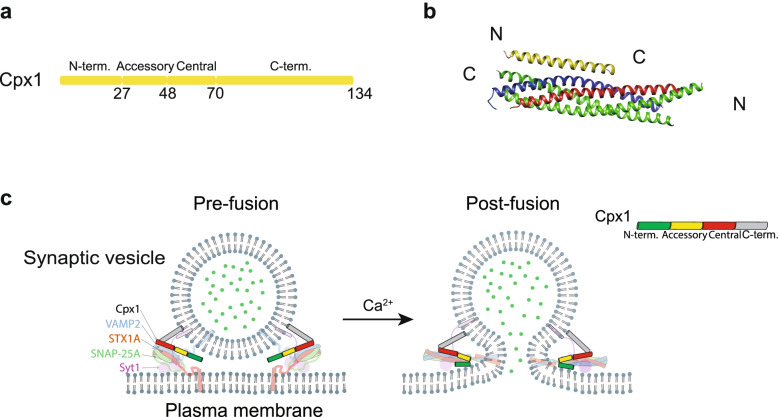
Fig. 5.
Cpx1 and its regulatory function. a Domain diagram of Cpx1. Residue numbers are indicated below the diagram. b Crystal structure of the SNARE-Cpx1 complex in Rattus norvegicus (PDB ID: 1KIL) [305]. c Models of how Cpx1 regulates synaptic vesicle fusion. In absence of Ca2+, the core fusion machinery is locked to a pre-fusion stage via several interactions from Cpx1: the central α-helical domain interacts with SNARE complex; the accessory α-helical domain involves in a tripartite interface with Syt1 and SNARE complex; C-terminal domain is associated with synaptic vesicle (left). When Ca2+ influx, Cpx1 inhibition could be released by a conformational change of the tripartite interface upon Ca2+ binding to Syt1, meanwhile Cpx1 synchronizes synaptic vesicle fusion via its N-terminal domain binds to C-terminus of trans-SNARE complex and plasma membrane (right)