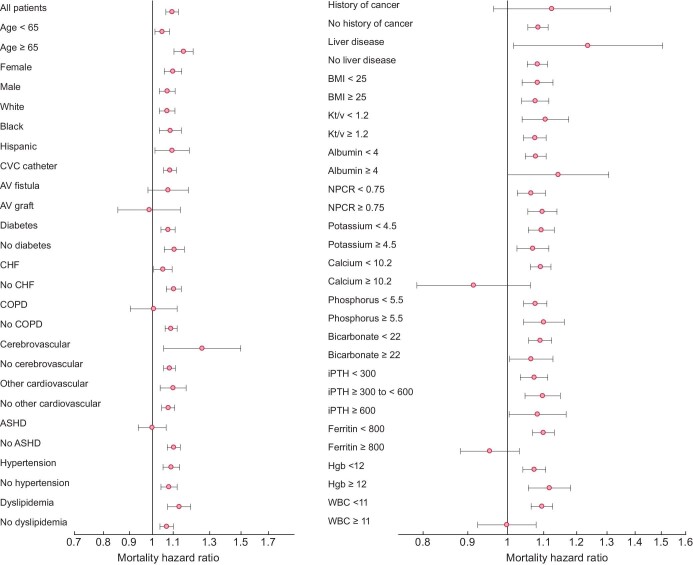
Figure 2:
Subgroup analyses examining the association of high serum globulin (≥3.2 g/dL) with all-cause mortality in the fully adjusted model among 104 164 hemodialysis patients. ASHD, atherosclerotic heart disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CVC, central venous catheter; AV, arteriovenous; CHF, congestive heart failure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; CBVD, cerebrovascular disease; HGB, hemoglobin; iPTH, intact parathyroid hormone; ISAT, iron saturation; KRU, residual urea clearance; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; NPCR, normalized protein catabolic rate; TIBC, total iron-binding capacity; WBC, white blood cell count; BMI, body mass index; HD, hemodialysis; spKt/V, single-pooled Kt/V.
Age in years; SBP and DBP in mmHg; weight in kg; albumin, hemoglobin and creatinine in g/dL; calcium, phosphorus and TIBC in mg/dL; ferritin in ng/mL; iPTH in pg/mL; bicarbonate and potassium in mEq/L; ALP and AST in IU/L; ISAT in %; WBC in ×103/mm3.