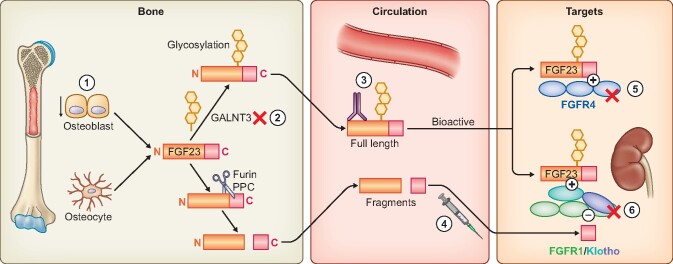
FIGURE 1.
Production and action of endocrine FGF23 and strategies to lower FGF23 bioactivity. 1. Reduce production. Achieved by reduction of P intake and absorption (see Figure 2) and pharmacologically by calcimimetics. 2. Inhibit glycosylation of newly synthesized FGF23 by small molecules. Glycosylation of FGF23 by GALNT3 (UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3) protects FGF23 from cleavage by furin proprotein convertase (PPC). Inhibition of GALNT3 results in accelerated FGF23 cleavage and clearance. 3. Neutralizing antibodies to circulating FGF23 reduce circulating active FGF23 4. Exogenous C-term fragment of FGF23 competitively blocks full-length FGF23 on-target action on the FGFR1–Klotho coreceptors (see Figure 3). 5. FGFR4 inhibitors block the off-target effects of FGF23 on FGFR4. 6. Pan-FGFR inhibitors block FGFR1–Klotho coreceptor complex and the other FGFRs.