Figure 1.
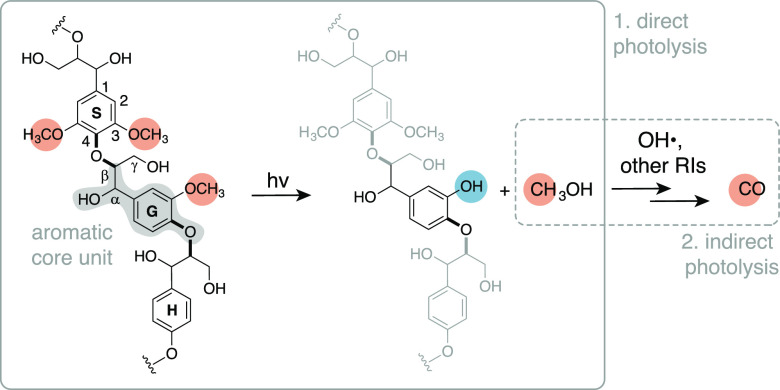
Schematic of the proposed two-step mechanism. This example shows the reactivity of a G unit, but a similar process can be anticipated for the S residue. The molecule on the far left depicts a possible structure of native lignin, with highlighted an aromatic G core unit (gray highlight), β-O-4 bonds (bold bonds), and aromatic methoxy groups (orange highlights). In native lignin, the α-carbon is typically an alcohol; this group can be converted to a ketone during (photo)oxidation.31,35 Letters H, G, and S indicate p-hydroxyphenyl, guaiacyl, and syringyl units, respectively. RIs is an abbreviation for reactive intermediates.