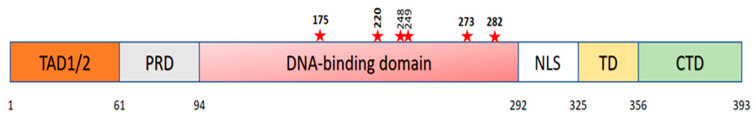
Figure 5.
Structure of p53 protein showing the different domains and hot spots (red stars) mutations occurring in human cancer. The 393 amino-acid p53 protein is depicted from the amino-terminus (1) to the carboxy-terminus (393) with boundaries for various domains shaded with different colors: transactivation domain (TAD1/2), proline-rich domain (PRD), DNA-binding domain (DBD), nuclear localization signal (NLS), tetramerization domain (TD), C-terminal domain (CTD).