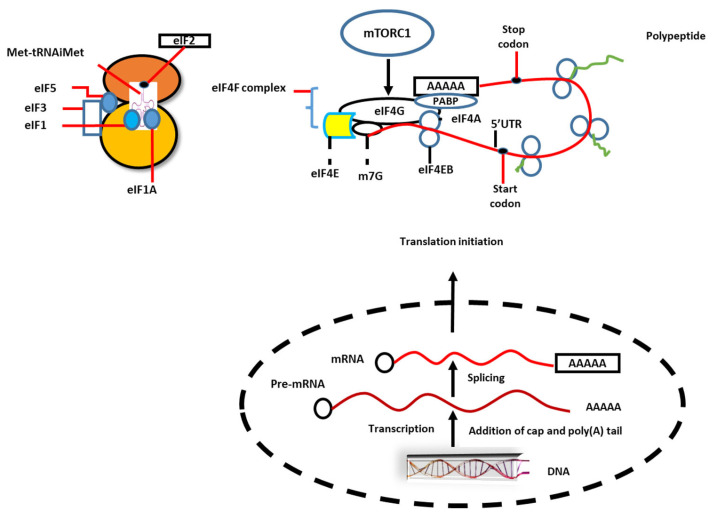
Figure 1.
Eukaryotic mRNA undergoes several steps of processing in the nucleolus, such as 7-methylguanosine (m7G) at the 5′ and poly A-tail in the 3′-end. Ribosomes are recruited by mRNA through coordinated multiple processes. Two protein complexes, eukaryote translation initiation factor (eIF4F), which comprises eIF4E (cap-binding protein), eIF4G (scaffold protein), and eIF4A (RNA helicase), and the ternary complex, which includes eIF2-GTP and initiation tRNA (Met-tRNAiMet), have pivotal roles in translation initiation. The mRNA circularization occurs in the interaction of eIF4G with poly A-tail binding protein (PABP). The eIF4F complex displays a secondary structure in the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of mRNA. The mTOR complex 1 controls the initiation of translation through the ternary complex and eIF4F complex. Moreover, the interaction of eIF4B with eIF4A increases the helicase activity of the latter.