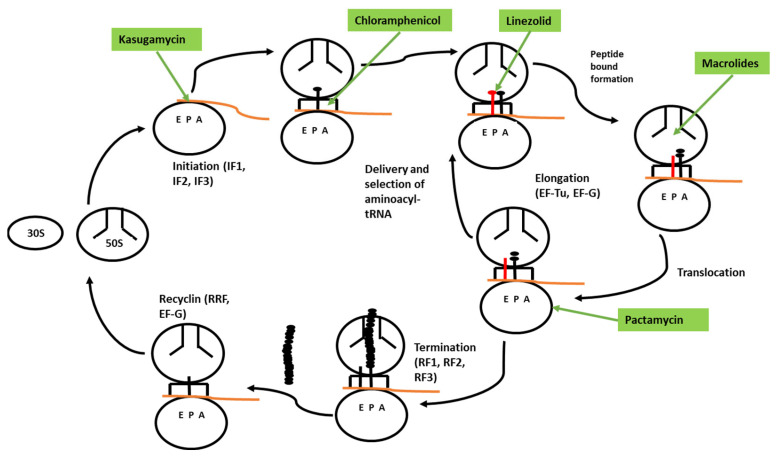
Figure 3.
Overview of protein synthesis in bacteria and inhibition by different antibiotics. First step: initiation of protein synthesis assisted by initiation factors (IF1, 2, 3), location of the start codon in mRNA, and connection of the initiation tRNA in the peptidyl (P) site. During translation elongation, EF-Tu-delivered aminoacyl-tRNA are selected and then accommodated in the aminoacyl tRNA. The antibiotic (green highlighted)- and macrolide-inhibition of peptide bond formation depends on the structure of the nascent protein. During translocation, the A site-bound peptidyl-tRNA moves into the P site, and the tRNA with a free 3′ end is relocated into the exit E site. When the ribosome encounters a stop codon, it enters the termination phase. During this phase, the completed protein is released with the help of termination factors (RF1 or RF2 and RF3). The last step is the recycling phase, when the combination of ribosome recycling factor (RRF) and EF-G splits the ribosome into its subunits.