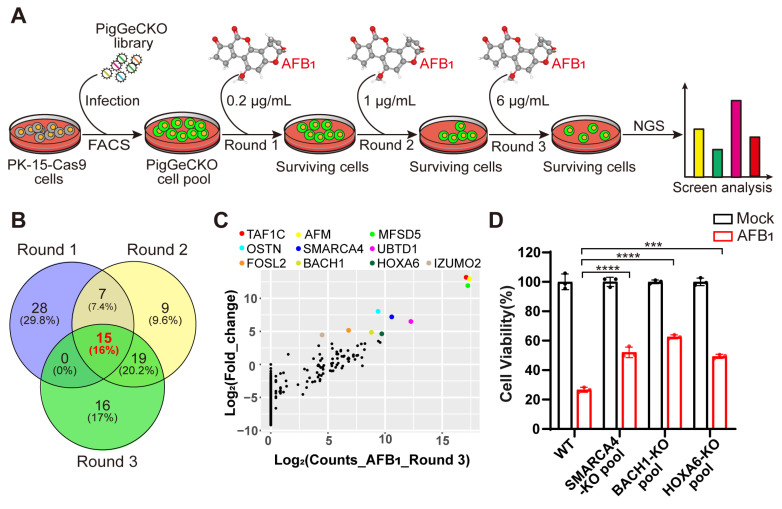
Figure 1.
Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9-based screening to identify genes involved in aflatoxin B1 toxicity. (A) Strategy for CRISPR/Cas9-based aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) resistance screening. PK-15 cells expressing Cas9 (PK-15-Cas9) were transduced with a lentiviral PigGeCKO library to generate a pool of mutant cells (PigGeCKO cell pool). Mutant cells were then subjected to sequential rounds of exposure to AFB1 at increasing concentrations (Round 1: 0.2 μg/mL, Round 2: 1.0 μg/mL, and Round 3: 6.0 μg/mL). AFB1 was refreshed daily until all control cells were killed. Surviving cells were harvested, and sgRNA sequences were identified by high-throughput sequencing. (B) Venn diagram of the top ~0.1% of shared and unique sgRNA target sequences obtained from each round of AFB1 screening. (C) Scatter plots of the frequencies of sgRNA target sequence and the extent of enrichment in transformed PK-15-Cas9 cells in Round 3 of AFB1 screening. (D) Cell viability assays for WT and KO cell pool of candidate genes after AFB1 exposure at 2 μg/mL for 36 h. *** p< 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. p values were determined with two-tailed Student’s t-tests. AFB1, aflatoxin B1; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; NGS, next-generation sequencing; Round 1 (2 or 3), the first (second or third) round of AFB1 challenge; WT, wild-type; KO, knockout.