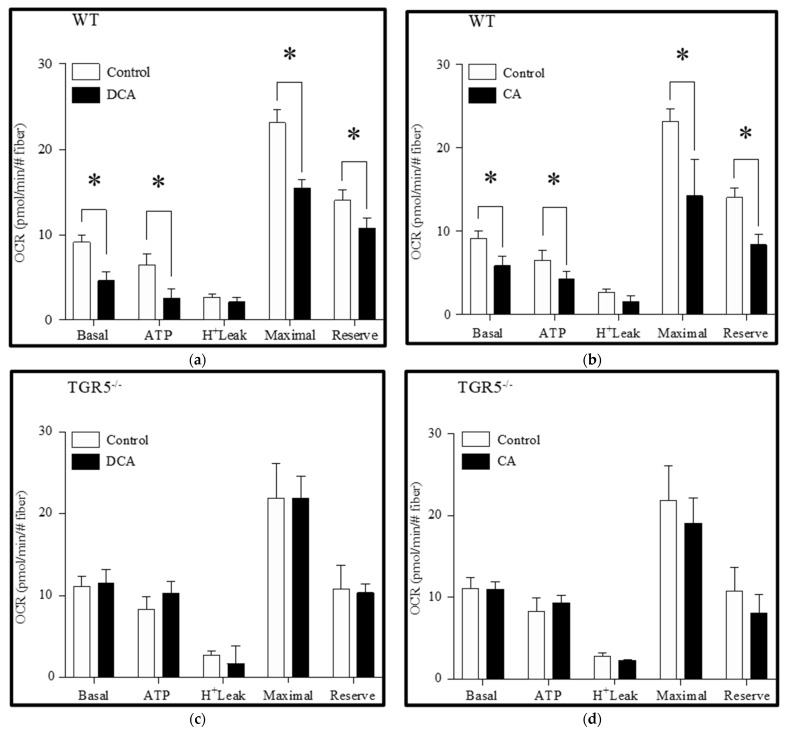
Figure 4.
Deoxycholic acid (DCA) and cholic acid (CA) decrease the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in muscle fiber through a TGR5-dependent mechanism. Skeletal muscle fibers from WT and TGR5−/− mice were incubated with DCA or CA for 72 h, and the basal, ATP-linked, H+-leak, maximal, and spare OCR were determined as described in the Materials and Methods section. (a,b) Analysis for OCR in WT fibers incubated with DCA (a) or CA (b). (c,d) Analysis for OCR in TGR5−/− fibers incubated with DCA (c) or CA (d). Values correspond to the mean ± SEM (n = 3, * p < 0.05, t-test).