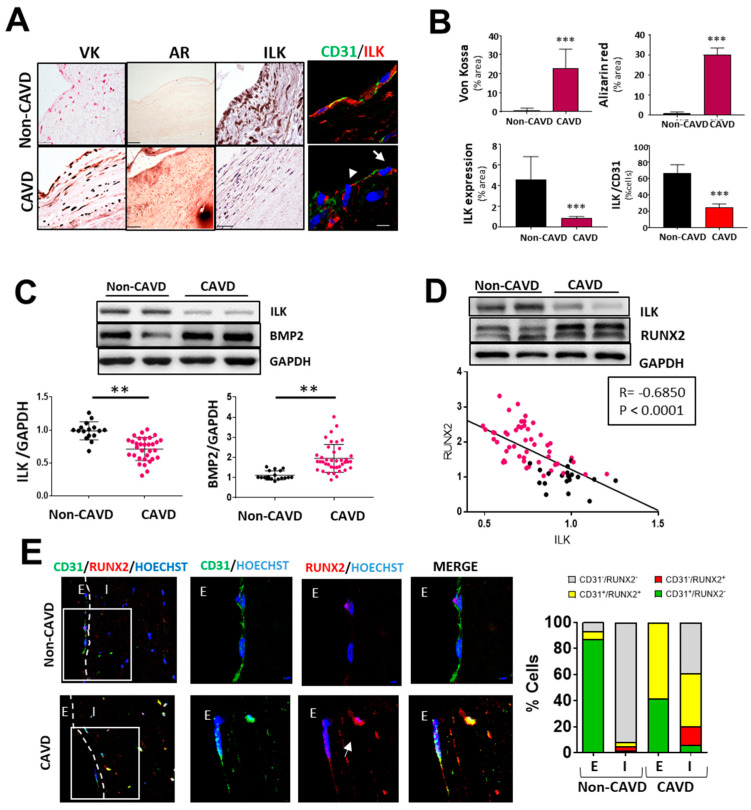
Figure 1.
Endothelial ILK is downregulated in calcific aortic valve disease. (A) Von Kossa (VK) and Alizarin Red (AR) staining of calcium deposits (left panel); immunohistochemistry of ILK (central panel); and immunofluorescence of ILK in red and the endothelial marker CD31 in green (right panel) in non-CAVD or CAVD human aortic valve leaflets. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. Arrows show valve endothelial cells. Scale bar = 25 µm. (B) Quantification of calcification and ILK expression shown in (A). n = 10. *** p < 0.001 vs. non-CAVD. (C,D) Western blot analysis of non-CAVD vs. CAVD valve tissue proteins. (C) ILK and BMP2 expression and quantification (n = 16–31, ** p < 0.01). (D) ILK and RUNX2 expression and Pearson correlation (R = −0.685, *** p < 0.0001, n = 72). (E) Confocal fluorescent microscopy images of CD31 (green) and RUNX2 (red) in non-CAVD and CAVD aortic leaflets. The dotted line delimits the endothelium (E) from the interstitium (I). Cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. On the right, magnifications of areas enclosed in white squares. Scale bar = 25 µm. Arrowheads indicate cells within the valves expressing both markers. Percentages of cells expressing CD31, RUNX2, or both markers are shown on the right. n = 4.