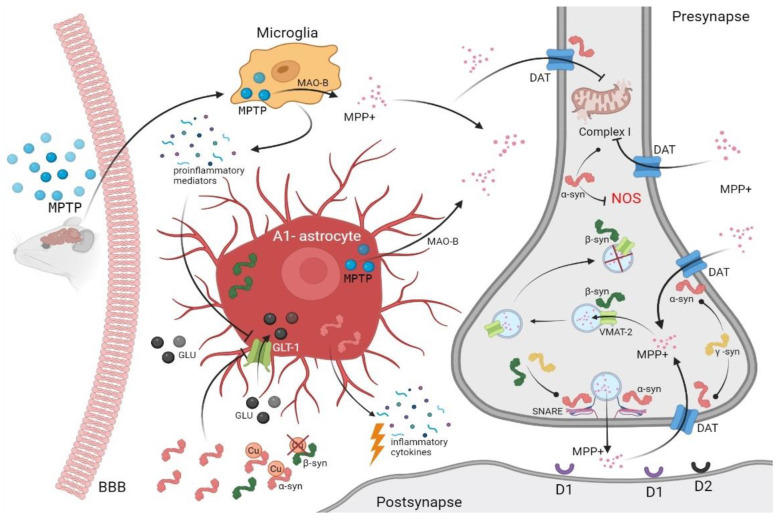
Figure 1.
The role of synucleins in the mechanisms of SNpc DA neurons during MPTP-induced parkinsonism. Key regulatory factors include the regulatory activity of all synucleins toward the presynaptic membrane of the dopamine transporter (DAT); increased DAT/VMAT-2 ratio and SNARE assembly due to the presence of alpha-synuclein and support from other members of the synuclein family; the inability of beta-synuclein in the presence of alpha- and gamma-synucleins to potentiate VMAT-2-dependent MPP+ capture to further sequester these molecules; the involvement of alpha-synuclein in the neuroinflammatory response; and glutamate toxicity induced by glial cells. These, as well as other unexplored effects of alpha-synuclein binding and penetration into damaged mitochondria, may have a special effect on the MPTP-induced death of DA neurons. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 2 November 2021).