Table 1.
Bioactive natural products against prostate cancer.
| Natural Compound | Constituent | Plant Source | Chemical Structure | Mechanism | Molecular Pathway (Reference) | In Vitro | In Vivo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Polyphenol | |||||||
| 1. 1 Polyphenol Flavonols | |||||||
| 1.1.1 Quercetin | Flavonol | Apple and onion |
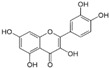
|
Induction of apoptosis. | PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK [6]; p21, FA, Hsp90 [7]. | LNCaP, DU 145, PC-3, Prostate cancer stem cells. | |
| 1.1.2 Apigenin | Flavone | Anthemis sp. |
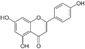
|
Induction of apoptosis and cell cycly arrest. | IGF-IR; PI3k/Akt [8]; HDACs [9]; ROS [10]; VEGF [11]. | PC-3 and 22Rv1. | 22Rv1 and PC-3 xenografts. |
| 1.1.3 Baicalin | Flavone | Genus Scutellaria |
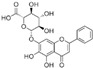
|
Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. | Caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR [12]; AR target genes [13]; Ezrin [14]. | DU 145 and PC-3. | PC-3 xenografts. |
| 1.1.4 Cyanidin-3-glucoside | Flavonoid anthocyanin | Berries, red cabbages, teas, and coloured grains. |
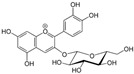
|
Inhibition of EMT. | Snail/E-cadherin [15]. | PC-3. | |
| 1.1.5 Daidzein | Isoflavone | Soybeans |
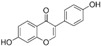
|
Induction of cell cycle arrest; CpG island demethylation. | CDK [16]; GSTP1 and EPHB2 [17]; ERβ [18]. | DU 145, LNCaP and PC-3. | |
| 1.1.6 Delphinidin | Flavonoid anthocyanin | Viola sp. |
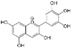
|
Inhibition of cell growth; Induction of apoptosis. | NF-κB [19]; β-catenin [20]; DR5 [21]; HDAC [22]. | PC-3 and LNCaP. | PC-3 xenografts. |
| 1.1.7 Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) | Catechin | Green tea |
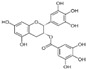
|
Suppression of the proliferation, invasion and migration, and vasculogenic mimicry; Induction of apoptosis and autophagy. | ERK1/2 [23], VEGF, uPA, angiopoietin 1/2, MMP-2, and MMP-9 [24], PSA [25], Caspase 9 [26]; Twist/VE-Cadherin/AKT [27]; AR [28]; CHOP and p-eIF2α [29]. | LNCaP, PC-3, 22Rv1. | PC-3 xenografts. |
| 1.1.8 Fisetin | Flavonol | Acacia greggii |
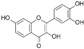
|
Inhibition of adhesion, migration, and metastasis; Induction of autophagy. | NF-κB [30]; mTOR and PI3K/Akt [31]; AR [32]; NF-κB [33]; Nudc [34]. | DU 145, LNCaP, PC-3. | CWR22 Rupsilon1 cells xenograft. |
| 1.1.9 Formononetin (FN) | Omethylated isoflavone | Trifolium pretense. |
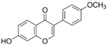
|
Induction of apoptosis. | ERK1/2, MAPK-Bax [35]; IGF-1/IGF-1R [36]; p38/Akt [37]; RASD1 [38]. | LNCaP, PC-3, and DU 145. | |
| 1.1.10 Genistein | Flavanone | Glycine max |
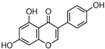
|
Inhibition of the proliferation; Suppression of cancer stem cells; Activation of epigenetic modification; Induction of apoptosis. |
IGF-1/IGF-1R [39]; miR-1260b [40]; miR-34a and HOTAIR [41]. | LNCaP, PC-3, and DU 145. | TRAMP mice. |
| 1.1.11 Glycyrrhiza | |||||||
| 1.1.11.1 Isoangustone A | Flavonoid | Glycyrrhiza uralensis |

|
Induction of apoptosis; G1 phase arrest. | Caspase [42]; CDK2/4, cyclin A [43]. | DU 145. | |
| 1.1.11.2 Licoricidin | Flavonoid | Glycyrrhiza uralensis |
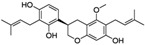
|
Inhibition of metastasis and invasion. | MMP, TIMP-1, VEGF [44]. | DU 145. | |
| 1.1.12 Licochalcone | Flavonoid | Licorice root |
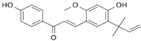
|
Induction of G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis. | Cyclin B1 and cdc2 [45]. | LNCaP, PC-3. | |
| 1.1.13 Luteolin | Flavone | Terminalia chebula |
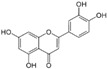
|
Suppression of angiogenesis; Induction of cell cycle arrest. | IGF-1 [46]; VEGF-2R, AR [47]. | LNCaP and PC-3. | PC-3 xenografts. |
| 1.2 Polyphenol lignans | |||||||
| 1.2.1 Arctigenin | lignan | Arctium lappa |
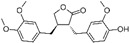
|
Inhibition of the proliferation; Induction of apoptosis and autophagy. | AR [48], FFA [49], PI3K/Akt/mTOR [50]. | LAPC-4 and LNCaP. | LAPC-4 xenograft. |
| 1.2.2 Honokiol | Lignin | Magnolia officinalis |
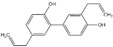
|
Induction of G0-G1 phase arrest and apoptosis; Inhibition of angiogenesis. | Bax, Bak, Bad, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 [51,52]. | LNCaP, PC-3, and C4-2. | PC-3 xenografts. |
| 1.2.3 Magnolol | Hydroxylated biphenyl lignan | Magnolia officinalis |
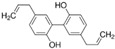
|
Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the adhesion, invasion, and migration. | EGFR [53]. | PC-3. | |
| 1.2.4 Obovatol | Biphenyl ether lignan | Magnolia obovate |
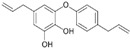
|
Induction of apoptosis. | NF-κB [54]. | LNCaP and PC-3. | |
| 1.2.5 Silibinin | Flavolignan | Silybum marianum |
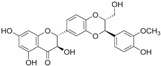
|
Induction of G1 phase arrest; Induction of apoptosis; Inhibition of EMT; Restriction of tumor microvessel density. | p21 and p27 [55]; NF-κB [56]; ZEB1 and SLUG [57]. | DU 145. | PC-3 xenografts and TRAMP mice [58]. |
| 1.3 Polyphenol Stilbenoids | |||||||
| 1.3.1 Resveratrol | Stilbenoid | Grape, raspberry, mulberry. |
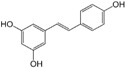
|
Induction of apoptosis; Cellular antioxidant defense. | FKHRL1 [59]; VEGF, MMPs [60]; CXCR4 [61]; ROS, RNS, HO-1 [62]; AR [63]. | TRAMP mouse [61]. | |
| 1.4 Other Polyphenols | |||||||
| 1.4.1 Curcumin | Polyphenols | Curcuma longa |
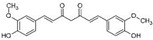
|
Induction of apoptosis; Induction of autophagy. | EGF-R [64]; AIF [65]; Wnt/β-catenin [66]; Nrf-2 [67]; MMPs [68]. | DU 145, LNCaP and PC-3. | LNCaP xenograft [69]; DU 145 xenografts [68]. |
| 1.4.2 Ellagitannins | Polyphenols | Pomegranate fruit |
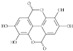
|
Induction of apoptosis and S phase cell cycle arrest; Inhibition of metastasis and angiogenesis. | SIRT1, p21, AIF [70]; Eicosanoid [71]; cyclin B1 and D1 [72]. MMP-2 [73]; p53-MDM2 [74]. | LNCaP, 22RV1 and PC-3. | murine studies [75]. |
| 1.4.3 Gallic acid | Polyphenols | Grape seed |
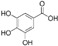
|
Induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest; Induction of apoptosis; Inhibition of invasion and migration. | cdc25A/C-cdc2 [76]; PARP [77]; p38, JNK, PKC, and PI3K/AKT [78]; Cdk, cyclin B1, and E [79]. | DU 145; PC-3. | TRAMP mice [79]; DU 145 and 22Rv1 xenografts [80]. |
| 1.4.4 Gossypol | Polyphenolic aldehyde | Cotton seed |
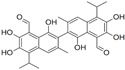
|
Induction of G0/G1 phase arrest; Induction of apoptosis; Induction of autophagy; Inhibition of angiogenesis; Reduction of the microvessel density. | TGF-β1 and Akt [81]; Bcl-xL [82]; Beclin1 [83]. AP-1, NF-κB [84]. | MAT-LyLu; PC-3. | PC-3 xenografts [85]. |
| 2. Terpenoids | |||||||
| 2.1 Artemisinin | Sesquiterpene | Artemisia annua |
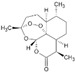
|
Induction of G1 cell cycle arrest; Inhibition of viability. | CDK4 and Sp1 [86], caspases 8/9 [87]. | LNCaP, DU 145 and PC-3. | |
| 2.2 Betulinic Acid (BA) | Triterpene | Betula papyrifera |
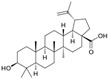
|
Induction of apoptosis; Inhibition of angiogenesis. | Bax/Bcl-2 [88], DUBs [89], AR and cyclin D [90]. | DU 145, LNCaP, and PC-3. | TRAMP mice [90]. |
| 2.3 Germacrone | Sesquiterpene | Geranium macrorrhizum. |
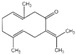
|
Induction of apoptosis and autophagy. | Akt/mTOR [91]. | PC-3 and 22RV1. | |
| 2.4 Ginsenosides | Steroid glycosides and triterpene saponins | Genus Panax |
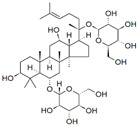
|
Inhibition of proliferation; Inhibition of migration and metastasis; Induction of apoptosis. | p38 [92]; MAP [93]. | PC-3M, LNCaP and PC-3. | PC-3 xenograft [94]. |
| 2.5 Glycyrrhizin | Saponins | Fabaceae |
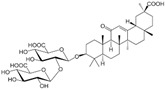
|
Induction of apoptosis and autophagy. | Apoptosis and autophagy [95]. | PC-3. | |
| 2.6 Lycopene | Carotenoid | Tomatoes |
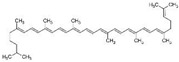
|
Reduction in cholesterol synthesis; Induction of apoptosis. | CDK7, EGFR, IGF-1R, and BCL2 [96]; PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1 [97]; CDK7,EGFR, IGF-1R, BCL2 [96]; IGF-I, IGF-IR, and IGFBP-3 [98]. | LNCaP, PC-3 and DU 145. | PC-3 xenograft [98]; TRAMP mice [99]. |
| 2.7 Oridonin | Isoprenoid | Rabdosia rubescens |
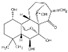
|
Induction of apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest; Induction of apoptosis, autophagy, and G2/M phase arrest. | p53 and Bax [100]; p21 [101]. | LNCaP and PC-3. | |
| 2.8 Thymoquinone (TQ) | Monoterpene | Nigella sativa |
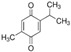
|
Induction of apoptosis; Inhibition of angiogenesis. | AR and E2F-1 [102]; ROS [103]; AKT, VEGF [104]. | LNCaP, PC-3, C4-B, and DU 145. | |
| 2.9 Ursolic acid (UA) | Pentacyclic triterpenoid | Cornus Officinalis |
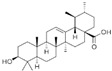
|
Induction of apoptosis. | Akt and MMP9 [105]; JNK [106]; CXCR4 [107]. NF-κB and STAT3 [108]; | PC-3, LNCaP, LNCaP-AI, and DU 145. | TRAMP mice [108]. |
| 2.10 β-Elemonic acid | Triterpene | Ganoderma tsugae, lucidum, and Boswellia. |
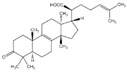
|
Induction of apoptosis. | JAK2/STAT3/MCL-1 and NF-κB [109]. | 22RV1. | 22RV1xenograft [109]. |
| 3. Taxanes | |||||||
| 3.1 Cabazitaxel | Taxane | European yew tree |
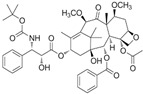
|
Inhibition of proliferation. | P-gp [110]. | C4-2. | |
| 3.2 Docetaxel | Taxane | European yew tree |
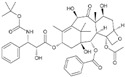
|
Induction of apoptosis. | p38/p53/p21 [111]. | LNCaP, PC3 and DU 145. | |
| 3.3 Paclitaxel | Taxane | Pacific yew tree |
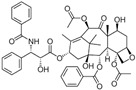
|
Induction of apoptosis. | Bcl-2 [112]; AR [113]. | C4-2. | 22Rv1 xenografts [113]. |
| 4. Alkaloids | |||||||
| 4.1 Anibamine, | Pyridine quaternary alkaloid | Aniba sp. |
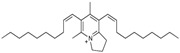
|
Inhibition of proliferation. | CCR5 [114]. | LNCaP. | |
| 4.2 Berberine | Isoquinoline Alkaloid | Genus Berberis |
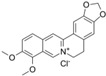
|
Induction of G1 phase arrest; enhancement of the radiosensitivity. | p53-p21 [115], AR [116], MAPK/caspase-3 and ROS [117]. | RM-1. | LNCaP xenografts [116]. |
| 4.3 Capsaicin | Alkaloid | Red pepper |
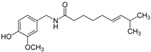
|
Induction of apoptosis. | JNK and ERK [118]. p53, p21, and Bax, AR [119]. | LNCaP, PC-3, and DU 145. | |
| 4.4 Neferine | Bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid | Nelumbo nucifera |
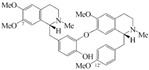
|
Inhibition of proliferation and migration of prostate cancer stem cells. | p38 mapk/jnk [120]. | PC3. | |
| 4.5 Piperine | Alkaloid | Black pepper |
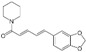
|
Induction of apoptosis, autophagy, and G0/G1 phase arrest. | NF-kB, STAT-3 [121]. | LNCaP, PC-3, and DU 145. | Animal xeno-transplanted model [122]; CRPC xenograft model [123]. |
| 4.6 Sanguinarine | Alkaloid | Sanguinaria Canadensis |
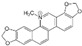
|
Inhibition of ubiquitin-proteasome system. | Stat3 [124], survivin [125], RGS17 [126]. | DU 145, C4-2B, and LNCaP. | DU 145 xenografts [125]. |
| 5. Other | |||||||
| 5.1 Gambogic acid | Xanthone | Garcinia hanburyi |
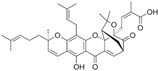
|
Inhibition of angiogenesis. | PI3K/Akt and NF-κB [127]; VEGF-2R [128]. | PC-3. | PC-3 xenograft model [128]. |
| 5.2 Glucoraphanin → Thiocyanates + Isothiocyanates + Indoles | |||||||
| 5.2.1 Sulforaphane (SFN) | Isothiocyanates (ITCs) | Cruciferous vegetables |
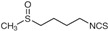
|
Induction of apoptosis; Induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest; Inhibition of FA metabolism. | ERK1/2 [129]; Hsp90 [130]; AR [131]; ROS [132]; FA [133]; HDACs [134]. | LNCaP, DU 145 and PC-3. | TRAMP mice [134]. |
| 5.2.2 Phenethyl-Isothiocyan (PEITC) | Isothiocyanates (ITCs) | Cruciferous vegetables |
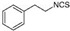
|
Induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest; Induction of apoptosis; Inhibition of angiogenesis. | α- and β-tubulin [135]; Bax [136]; Akt [137]; PECAM1-CD31 [138]. | C4-2B, DU 145, PC-3, and LNCaP. | LNCaP xenograft model [138]; TRAMP mice [139]. |
| 5.2.3 Indole-3-Carbinol | Indoles | Cruciferous vegetables |
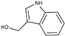
|
Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest; Modulation of epigenetic alterations of cancer stem cells. | Bax [140]; NF-ĸB, Nrf2 [140]. | LNCaP, and PC-3. | |
