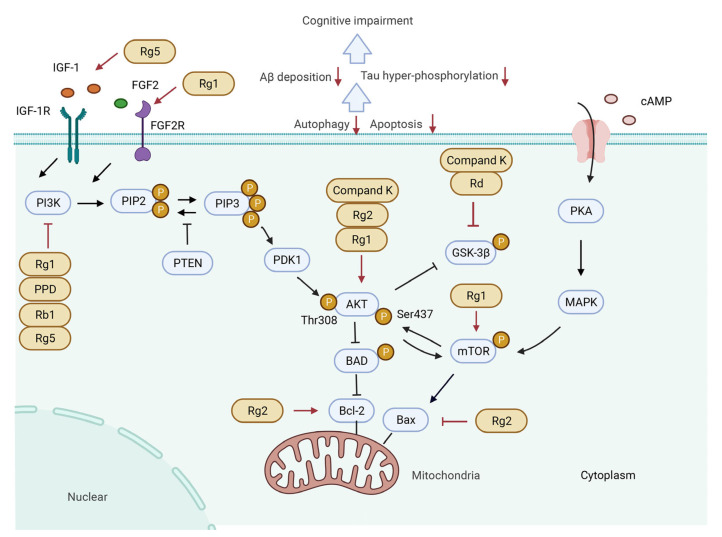
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms of regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by ginsenosides in treating cognitive impairment in the pathological model. (1) Rg5 and Rg1 activate PI3K/AKT pathway by stimulating IGF-1 and FGF2, perhaps eventually reducing Aβ deposition and tau hyperphosphorylation by inhibiting GSK-3β. Moreover, compound K, Rg2, and Rg1 can activate phosphorylation of AKT to reduce the content of GSK-3β. In addition, compound K and Rd directly attenuate GSK-3β to further inhibit Aβ deposition and tau hyperphosphorylation. (2) PI3K can be inhibited by Rg1, PPD, Rb1, and Rg5, further promoting the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, and increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio to attenuate cell apoptosis. Additionally, Rg2 can directly promote the expression of Bcl-2. (3) Rg1 increases the expression of p-Akt and p-mTOR to inhibit mTOR-medicated autophagy.