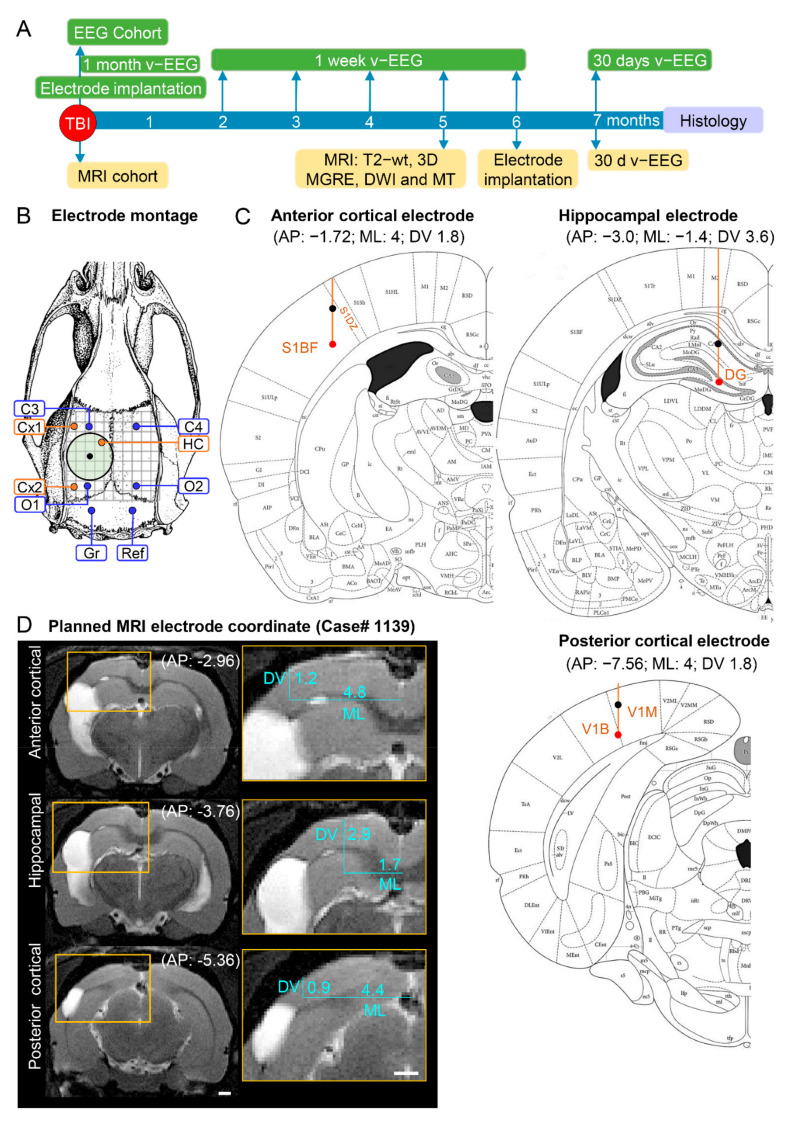
Figure 1.
Study design, electrode montage, and atlas or MRI-planned electrode coordinates. (A) Study design. Following TBI, rats were divided into either the EEG or MRI cohort. The rats of the EEG cohort were implanted with electrodes after fully righting themselves following induction of TBI. The rats were followed up immediately afterward with 1 month video-EEG and then for 1 week monthly until the 6th post-TBI month. The rats of the MRI cohort were magnetic resonance-imaged at 5 months post-TBI and T2-wt images were used to calculate the coordinates of the intracerebral electrodes implanted at 6 months post-TBI. Both cohorts were continuously monitored with video-EEG for 30 days at 7 months post-TBI to diagnose epilepsy. At the end of the 7-month follow-up period, all rats were euthanized and the brains processed for histological identification of the location of the intracerebral electrodes. (B) Electrode montage used in the study. Four epidural screw electrodes (C3, C4, O1 and O2), 3 intracerebral bipolar wire electrodes (anterior cortical Cx1, posterior cortical Cx2, and hippocampal HC), a ground (Gr) and reference (Ref) electrode. (C) Atlas plates demonstrating the planned coordinates used in the EEG cohort to implant the anterior cortical, hippocampal, and posterior cortical electrodes. The black dot refers to the upper tip and the red dot to the lower tip of the bipolar electrode (1 mm apart). Reprinted/adapted with permission from [25]. 2007, Elsevier Inc. (D) MRI T2-wt images of rat 1139 demonstrating the planned-MRI coordinates of the intracerebral anterior cortical, hippocampal, and posterior cortical electrodes. The anteroposterior (AP) coordinate was determined by aligning the MR images with the atlas [25]. The mediolateral (ML) and dorsoventral (DV) coordinates were determined using ImageJ software (version 1.47v, Wayne Rasband and contributors, National Institute of Health, USA).