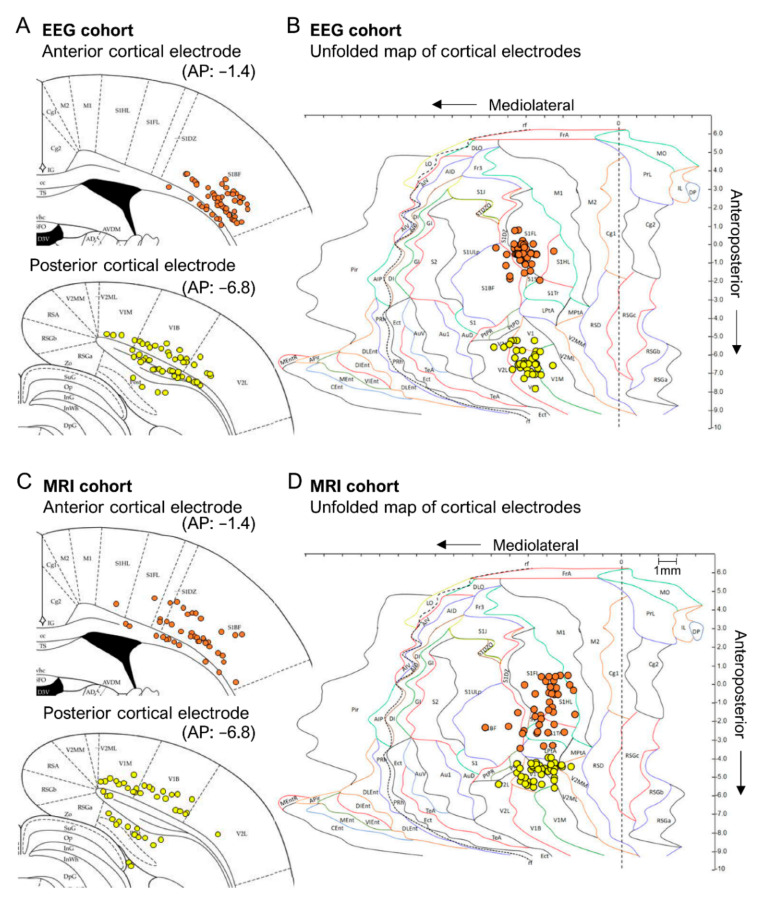
Figure 4.
Location of the lower tip of the anterior and posterior intracortical electrodes on atlas plates and unfolded cortical maps. (A) In the EEG cohort (upper panel), the dorsoventral (DV) location of at least 1 of the tips of all anterior bipolar electrodes (atlas plate: bregma −1.4 mm) was within the primary somatosensory cortex (S1) and that of the posterior electrode (lower panel; atlas plate: bregma −6.8 mm) was within the visual cortex. Each dot represents 1 bipolar electrode. (B) An unfolded map (UFM) showing the location of electrode tracks in the EEG cohort as seen from the surface of the brain. The intersection of the electrode path with cortical layer V was used as reference. The UFMs confirmed the location of the anterior electrode paths in the S1 and posterior electrode paths in the visual cortex. (C) Atlas plate showing the DV locations of the anterior (upper panel) and posterior (lower panel) intracortical electrodes in the MRI cohort. As in the EEG cohort, the anterior electrode was in S1 and the posterior electrode was in the visual cortex. (D) A UFM showing the location of electrode tracks in the MRI cohort as seen from the surface of the brain. All electrode tracks were within S1 or the visual cortex. Note that in the MRI cohort, we used the 5-month in vivo MRI to adjust the electrode coordinates to target the perilesional cortex and to avoid lesion cavities, underlying brain areas, or ventricles. As expected, this resulted in a more heterogeneous distribution of electrode paths than in the EEG cohort with atlas-based fixed coordinates. Atlas plates and UFMs were generated using the Paxinos rat brain atlas (6th edition).