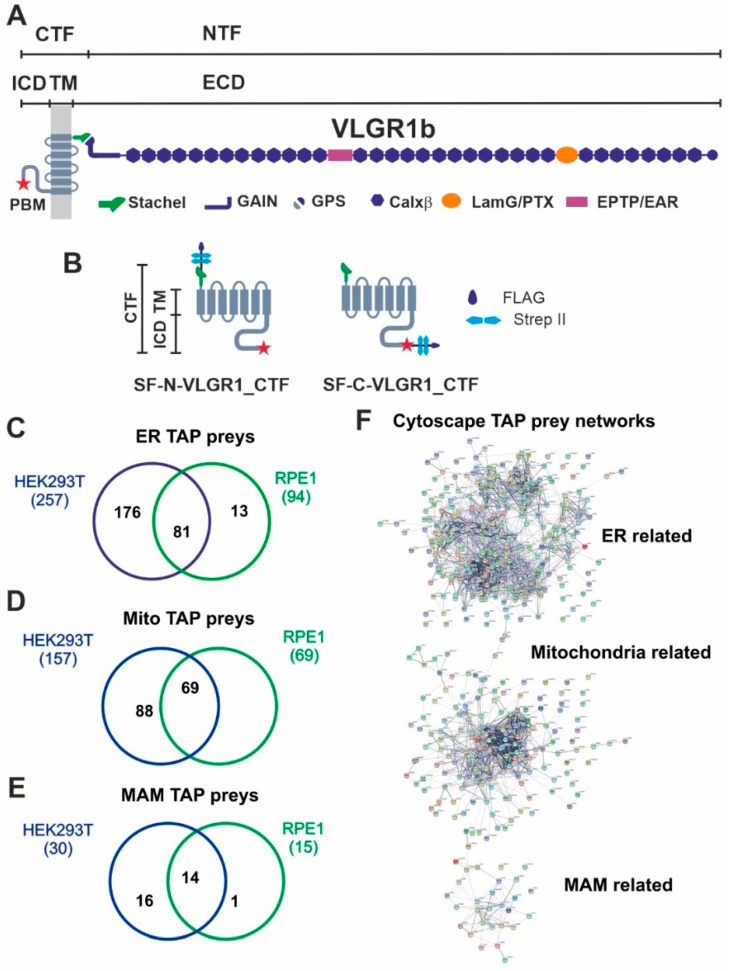
Figure 1.
VLGR1 protein domain composition, VLGR1_CTF constructs for TAPs and overlap of proteins associated to ER, mitochondria and MAM identified in VLGR1_CTF TAPs. (A) VLGR1 protein domain composition: VLGR1 molecules consist of a C-terminal fragment (CTF) and a N-terminal fragment (NTF) which result from the cleavage at the highly conserved GPCR proteolytic site (GPS) in the GAIN (autoproteolysis-inducing) domain positioned next to the seven-span transmembrane domain (TM). After autoproteolytic cleavage the first 11 amino acids of VLGR1_CTF, the so-called Stachel peptide, can act as a tethered internal agonist for receptor activation [3]. The extracellular domain (ECD) of VLGR1b contains numerous Ca2+ binding calcium exchanger β motifs (Calx-β), seven epilepsy-associated/Epitemptin-like (EAR/EPTP) repeats and a pentaxin/laminin G-like domain (LamG/PTX). The intracellular domain (ICD) ends with a class-1 PDZ binding motif (PBM). (B) VLGR1_CTF, N- or C-terminal tagged with Strep II/FLAG (SF)-tag used as baits in TAPs. (C) Venn diagram shows an overlap of 81 proteins of ER-related TAP prey for polled VLGR1_CTF N-and C-terminal tagged TAPs from HEK293T and hTERT-RPE1 cells. (D) Mitochondria-related prey proteins from VLGR1_CTF N-and C-terminal tagged TAPs in HEK293T and hTERT-RPE1 cells, compared in a Venn diagram with an overlap of 69 proteins. (E) 14 common MAM prey proteins are identified in TAPs from HEK293T and hTERT-RPE1 cells. (F) Protein networks of ER, mitochondria and MAM-related proteins, illustrated by Cytoscape analysis of preys identified in VLGR1_CTF N-and C-terminal tagged TAPs.