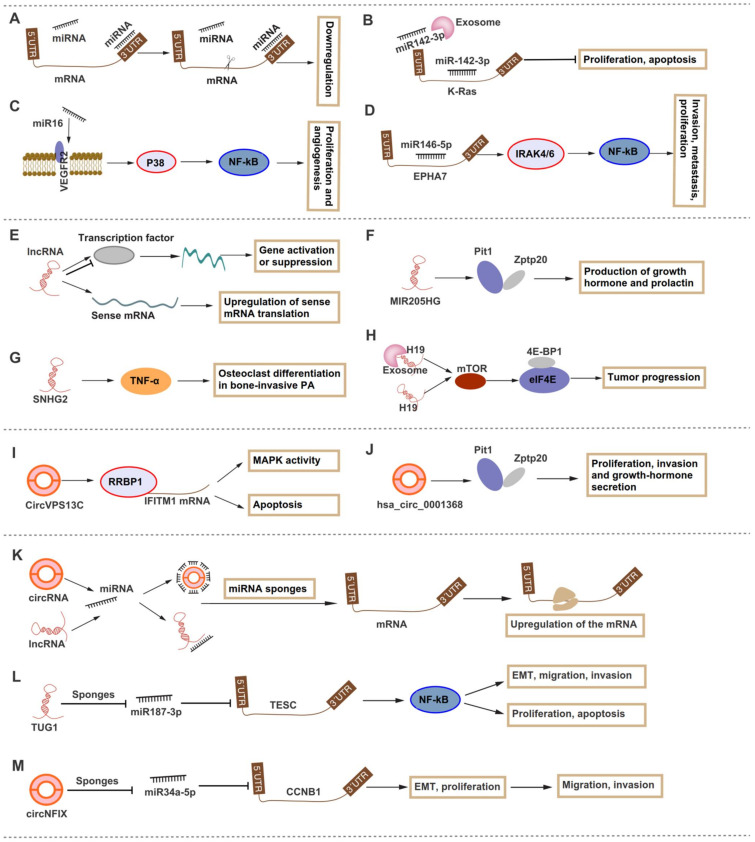
Figure 1.
The potential mechanisms of non-coding RNAs in pituitary adenoma. (A) miRNA inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 3’-UTR of mRNA. (B–D) miR-142-3p, miR-16, miR-146-5p, and exosome-derived miR-146-5p are involved in the pathogenesis of pituitary adenoma (PA). (E) LncRNA regulates gene activation or suppression by increasing or decreasing transcription via the transcription factor, respectively; antisense lncRNA upregulates the sense mRNA translation process. (F–H) MIR205GH, SNHG24, H19, and exosome-derived H19 are involved in the pathogenesis of PA. (I–J) CircVPS13C and hsa_circ_0001368 are involved in the pathogenesis of PA. (K) CircRNA and lncRNA increase the translation process and protein production via sponging miRNA. (L) LncRNA TUG1 modulates PA progression by regulating the TESC–NF-kB pathway via sponging miR-187-3p. (M) CircNFIX promotes PA progression by regulating CCNB1 via sponging miR-34a-5p.