Figure 1.
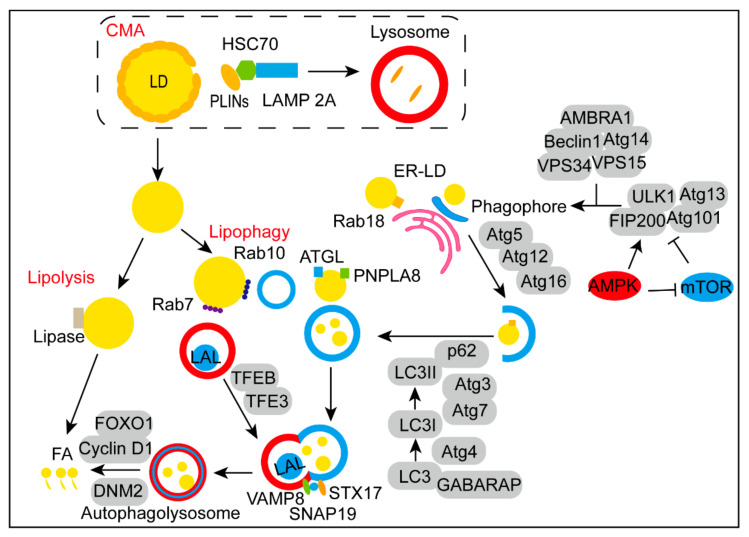
Steps of LDs degradation. After the degradation of PLIN2 and PLIN3 in lysosome via CMA mediated by HSC70, LDs are exposed for lipolysis and lipophagy. The activation of AMPK and mTOR recruits ULK1-Atg13-FIP200-Atg101 complex to trigger the initiation of autophagy. Next, the initiation complex composed of Beclin1, Atg14, VPS34, VPS15, and AMBRA1 is activated to form the origin of phagophore. Rab18 is essential in the spatiotemporal dynamic of ER-LD. During the elongation progress, the Atg5-Atg12-Atg16 complex promotes the autophagic vesicle formation. Simultaneously, Atg3, Atg4 and Atg7 are involved in the lipid-soluble form of LC3. Receptors such as p62 facilitate the localization of LC3-II on the autophagic membrane. On the surface of LDs, ATGL and PNPLA8 were identified as mammalian lipid receptors. Rab10 recruits LC3-positive phagophores to the circumference of LD, while Rab7 promotes the tethering and fusion of autophagosomes to lysosomes. TFEB and TFE3 are key regulators in autophagosome maturation and lysosomal biogenesis. Then, the VAMP8-SNAP29-STX17 complex mediates the form of autolysosome. Finally, LDs in the autolysosome degraded to FAs by LAL and regulated by FOXO1, Cyclin D1 and DNM2.