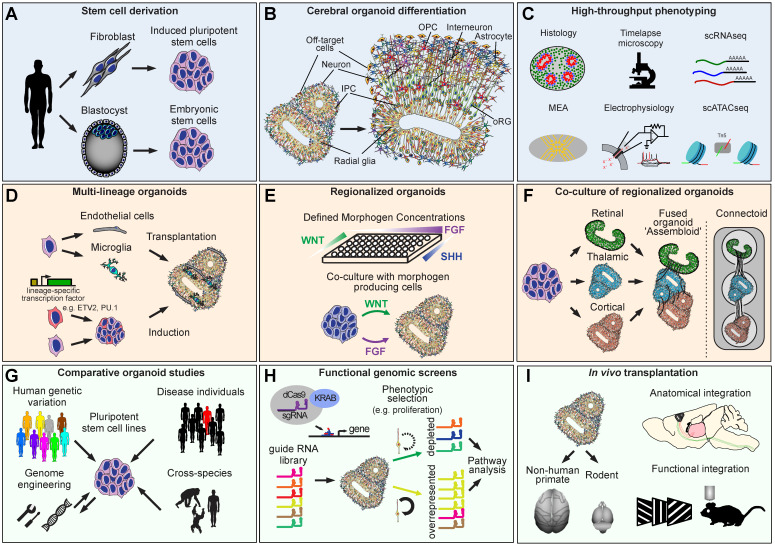
Figure 1.
Derivation, refinement, and applications of cerebral organoid technologies. (A) Pluripotent stem cells can be derived from embryonic material or somatic cells. (B) Cerebral organoids recapitulate key cell types of the developing brain. (C) Scalable organoid characterization technologies. (D) Multi-lineage organoids can be derived to recapitulate tissue cell type diversity more completely. (E) Improved regional specificity can be achieved by manipulating developmental signaling pathways according to the blueprint of normal developing tissue. (F) Interactions between brain regions can be modeled using co-cultured organoids. (G) Organoids derived from different sources of pluripotent stem cells can be used to compare developmental trajectories across individuals, species, or disease states. (H) Functional genomic screens can be used to map the genetic architecture of biological phenotypes relevant to neural development. (I) Combining organoids with animal models to advance future regenerative medicine applications.