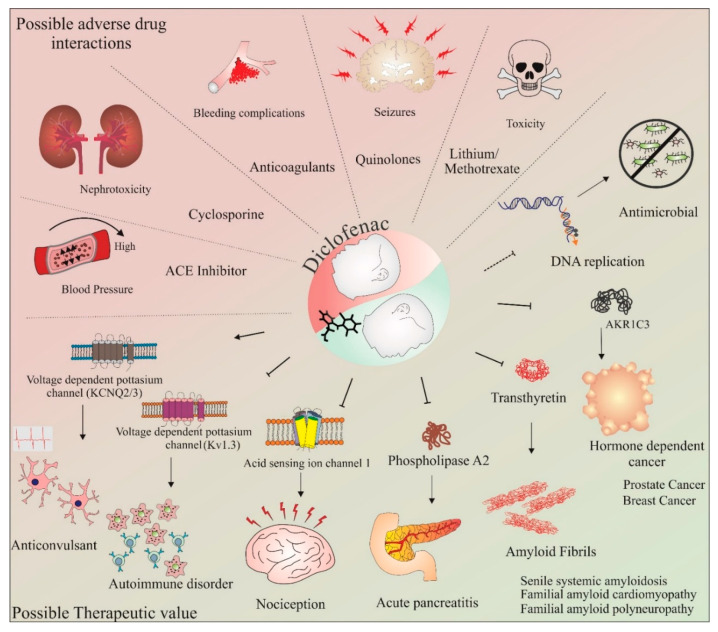
Figure 2.
Therapeutic value and adverse drug–drug interactions of diclofenac. The potential use of diclofenac in combination therapies targeting various conditions has been assessed in numerous studies. However, some combinations of drugs with diclofenac have shown adverse effects. These include diclofenac in combination with ACE inhibitors, cyclosporine, anticoagulants, quinolones, and lithium/methotrexate. These combinations have resulted in increased blood pressure, nephrotoxicity, bleeding complications, seizures, and toxicity, respectively. In addition, with regard to its anti-inflammatory effects, studies have shown the therapeutic value of diclofenac in various diseases and conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, nociception, pancreatitis, amyloid fibril formation, seizures, cancer, and as an antimicrobial agent. The activation/formation and inhibition are depicted with arrows and blunt heads, respectively. The dotted blunt end represents an inhibitory effect that requires further investigations on diclofenac’s mechanism of action.