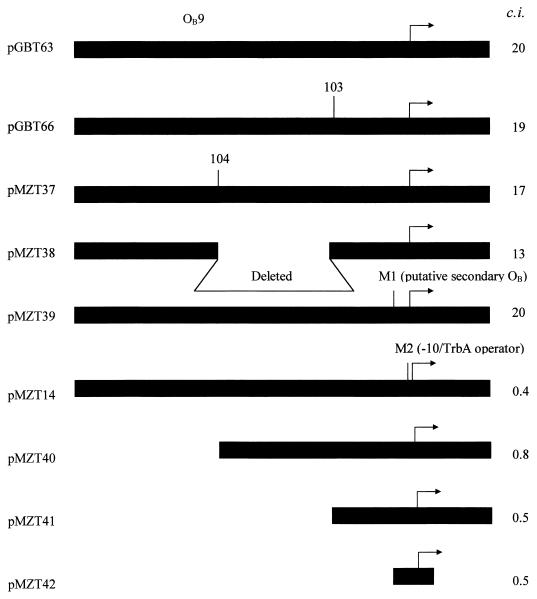
FIG. 3.
Genetic analysis to determine whether the presence of both TrbA and KorB binding sites are necessary for cooperative repression of trbBp. Arrows indicate trbBp which is fused to xylE. M1, mutations in the putative degenerate KorB operator (Fig. 2); M2, mutation in the −10 region of trbBp which also reduces sensitivity to trbA repression (Fig. 2); OB9, the known KorB operator; 103 and 104, EcoRI sites in a 35-bp segment left as a result of Tn1723 transposon insertion followed by deletion of the internal EcoRI fragment which is defined by EcoRI sites 15 bp from each end of the transpsoson (20). c.i., cooperativity in vivo index when KorB was expressed from pDM1.21 (pDM1.2 as control) and TrbA was expressed from pMZT24 (pGBT30 as control). Repressor expression was induced with IPTG as indicated in Table 2.