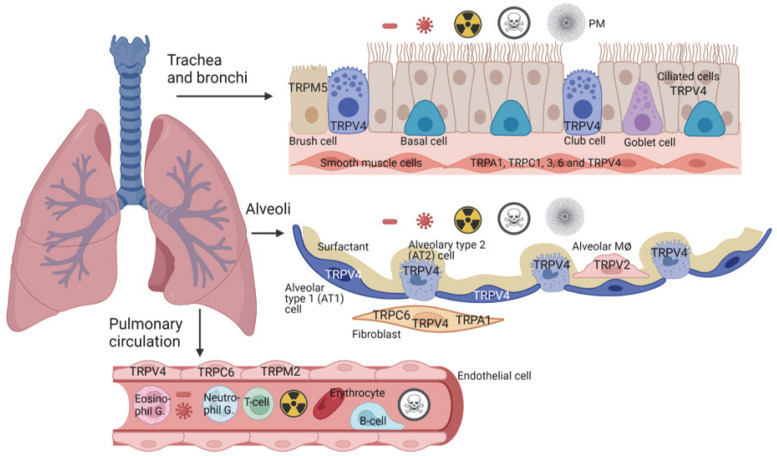
Figure 1.
Cells of the human and murine respiratory tract and TRP channel function. The upper part of the lower airways with basal, goblet, club and ciliated cells as well as the alveolus and the pulmonary vasculature are shown. Functional active TRP channels based on reported data are indicated. In the very specialized brush cells TRPM5 channels are exclusively active. In the alveoli, alveolar type 1 (AT1) cells are important for barrier function, while AT2 cells secrete a surfactant that can renew damaged AT1 cells. Alveolar and interstitial macrophages (MØ) are able to phagocytize microorganisms and particulate matter (PM). Fibroblasts involved in wound healing own TRPC6 and TRPA1 proteins. The latter channel, however, exists only in human and not in mouse fibroblasts. Endothelial cells as natural barrier to exclude toxicants perfused in the blood need active TRPC6, TRPM2 and TRPV4 channels. PM, particulate matter. See also Table 1 for single-cell mRNA expression data and the text for more details.