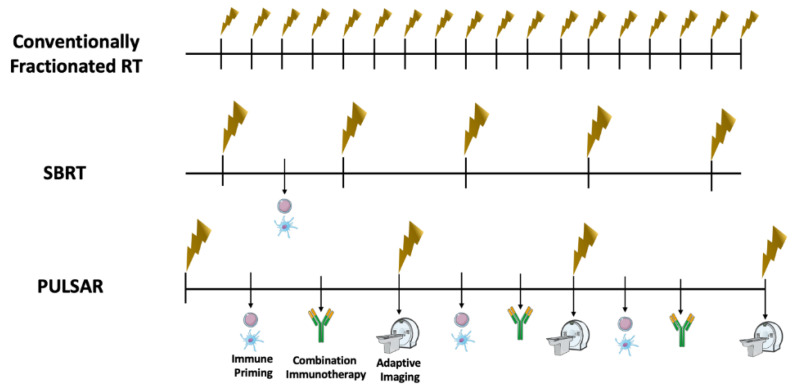
Figure 2.
Potential Advantages of PULSAR Compared to Traditional Radiation Schema. Conventionally Fractionated radiation is characterized by daily treatments of non-ablative doses of radiation, that rarely lead to sufficient immune-stimulatory effects. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy has the potential to offer ablative doses of radiation in 1 to 5 fractions, and may lead to sufficient immune priming to enhance anti-tumor immune response. However, with this approach there is no adaptation to changes in tumor anatomy between treatments, and considering a regular schedule of treatment that is typically every other day there is rarely combination with immunotherapy in between treatments. In personalized ultra-hypofractionated adaptive radiotherapy (PULSAR), pulses of ablative treatment can be delivered 2 weeks or even 1 month apart, with immune priming and immunotherapy administration regularly occurring between pulses to synergize for optimal anti-tumor effect. Furthermore, imaging prior to each pulse is acquired for personalized adaptation to tumor changes in anatomy over time.