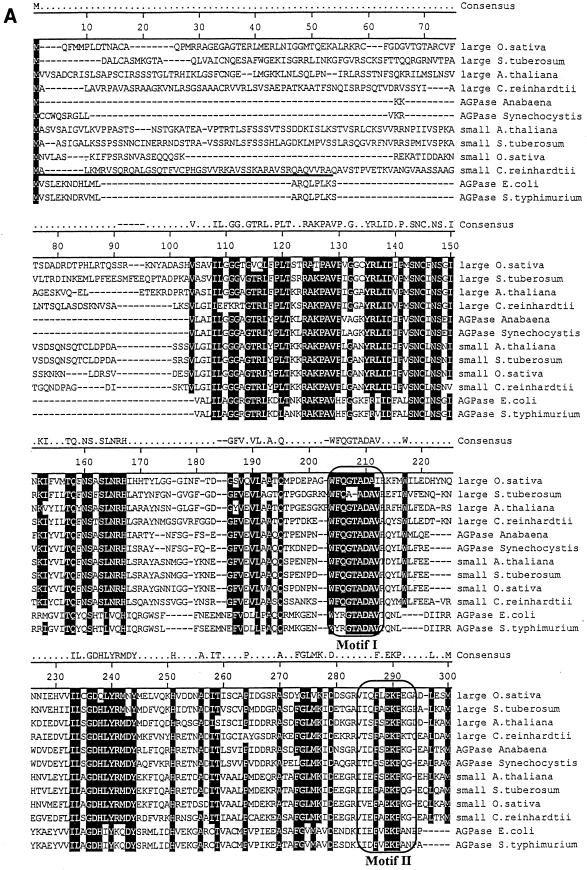
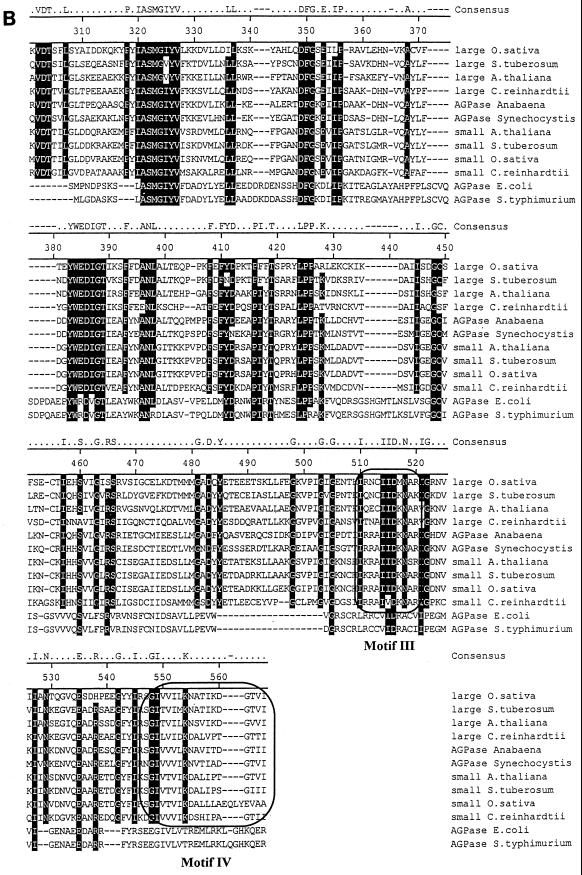
FIG. 3.
Protein sequence of the small subunit of Chlamydomonas ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Shown is a comparison of the algal protein sequence to those of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase subunits of Oryza sativa, Solanum tuberosum, A. thaliana, E. coli, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Large and small correspond to the large and small subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, respectively. Accession numbers (top to bottom) are as follows: AAB58473, P55242, BAA76362, X91736, P30521, BAA18822, AAB09585, P23509, P15280, AF193431, P00584, and P05415. The putative transit peptide of the Chlamydomonas small ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase subunit is underlined. Its cleavage site remains hypothetical since it varies from that of the large subunit, and we have been unable to sequence the N terminus of the purified small subunit (15). The framed boxes marked Motif I and Motif II (A) represent, respectively, the regions considered to be involved in the binding to ATP and glucose-1-phosphate. The domains contained within the framed boxes marked Motif III and Motif IV (B) are considered to be involved in the binding to 3-PGA in plants. The consensus amino acids shaded in black are those identical in at least 10 of 12 sequences. The figure was constructed using the Clustal method with the PAM250 residue weight table.