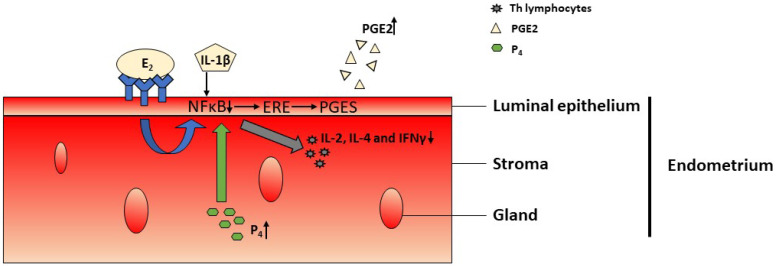
Figure 2.
Changes during pregnancy development. Elevated levels of estradiol (E2) together with interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and progesterone (P4) reduce nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) activation, leading to an increase in the activity of estrogen response elements (ERE) in the DNA of endometrial luminal epithelium. This triggers an increase in the expression of prostaglandin E synthase (PGES) and production of prostaglandin E (PGE2). Reduced NFκB activation causes the inhibition of interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 4 (IL-4) and interferon gamma (IFNγ) production in T lymphocytes. ↑: increase; ↓: decrease.