FIG. 2.
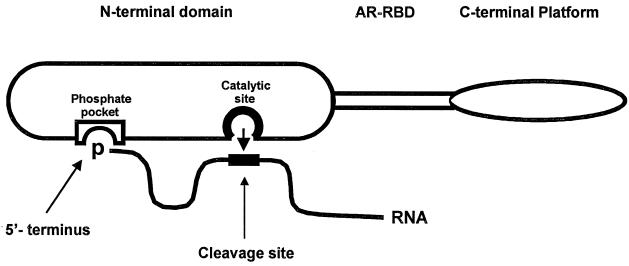
Simple model for recognition of p-RNAs by RNase E. The three domains of RNase E include the N terminus with catalytic activity, the central arginine-rich RNA binding domain (ARRBD), and the C-terminal “platform” with interaction sites for RhlB, enolase and polynucleotide phosphorylase (not shown) (23). For simplicity, RNase E is drawn as a monomer, but its quaternary structure is unknown. The RNA substrate is shown by a solid line thickened at a potential RNase E cleavage site. RNA sequences between the 5′ end and the site of cleavage are presumed to loop away from the surface of the enzyme. The nucleophilic attack on the phosphodiester bond is shown by the short arrow. The putative phosphate-binding pocket and the active site for catalysis are presumed to be separate sites within the N-terminal domain of the enzyme (see the text).