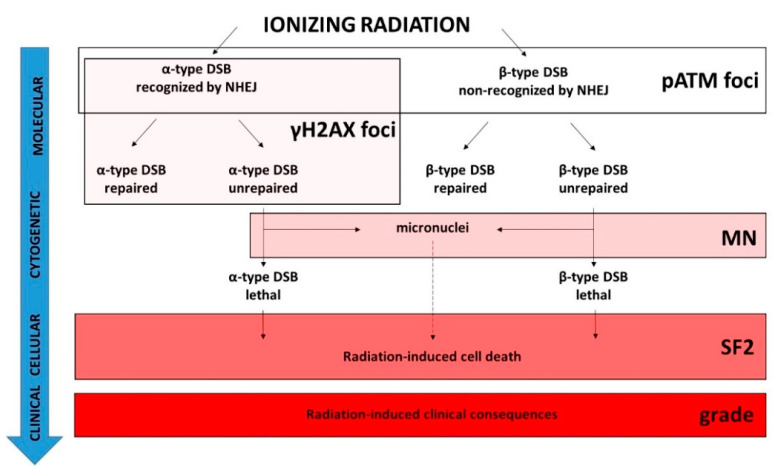
Figure 9.
Schematic view of the molecular, cytogenetic, cellular, and clinical consequences of exposure to IR and the validity domain of the major radiosensitivity endpoints. IR induces two types of DSB. The α-type DSBs are recognized by the NHEJ DSB repair pathway while the β-type DSBs are not [49]. For each type of DSB, there are some subsets of unrepaired DSB [49]. Among them, some may be unrepairable and contribute to the lethal effect. Some unrepaired DSBs may also provide micronuclei according to the radiosensitivity status and the capacity of irradiated cells to bypass the G2/M arrest [15]. The pATM foci biomarker detects the DSBs recognized by NHEJ, and the DSBs non-recognized by NHEJ or recognized by another DSB repair pathway can be deduced from the induction rate of DSBs “physically” induced by IR. The γH2AX foci biomarker detects the α-type DSBs only. Both α- and β-type unrepaired DSBs may provide some micronuclei, but the ratio between unrepaired DSBs and micronuclei is not necessarily equal to 1. Some subsets of micronuclei can contribute to the lethal effect. SF2 reflects all the RI cell deaths and therefore reflects the whole cellular response to IR independently of the DSB repair pathways involved. The dashed line indicates that the link is different from a one-to-one correlation.