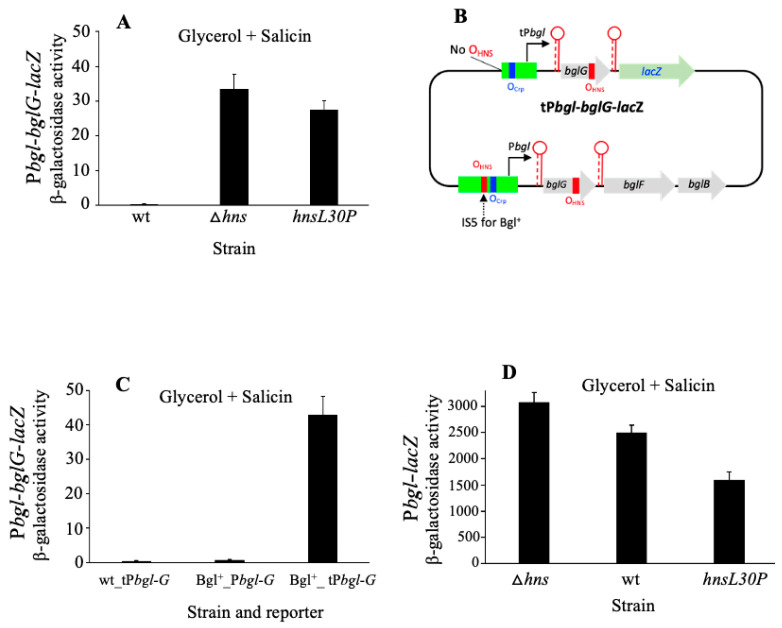
Figure 6.
Possible requirement of DNA looping for bgl operon silencing. (A) Effect of H-NSL30P on bgl operon expression. H-NSL30P is an H-NS derivative that carries a proline residue instead of leucine at residue 30 in the protein. This derivative is thought to maintain its DNA-binding capability but is deficient in oligomerization [64,65], thereby failing to bridge two or more DNA loci together. Using the operon reporter, Pbgl-bglG-lacZ, the effect of this mutant H-NS on bgl operon expression was determined by comparing the wild type H-NS and the absence of H-NS. (B) Diagram of a truncated bgl operon reporter (tPbgl-bglG-lacZ). It is the same as the regular operon reporter Pbgl-bglG-lacZ except that the regulatory region upstream of the Crp operator (believed to carry an H-NS binding site) in Pbgl has been removed. The blue bars represent the Crp binding sites (OCrp) while the red bars represent the proposed H-NS binding sites (OHNS). (C) The bgl operon activity using a reporter lacking the proposed H-NS binding site in the upstream regulatory region. (D) Effect of H-NSL30P on Pbgl. In (A,C,D), test strains were cultured in M63 with glycerol and salicin as carbon sources at 37 °C. Sample collection and β-galactosidase assays were carried out as in Figure 1.