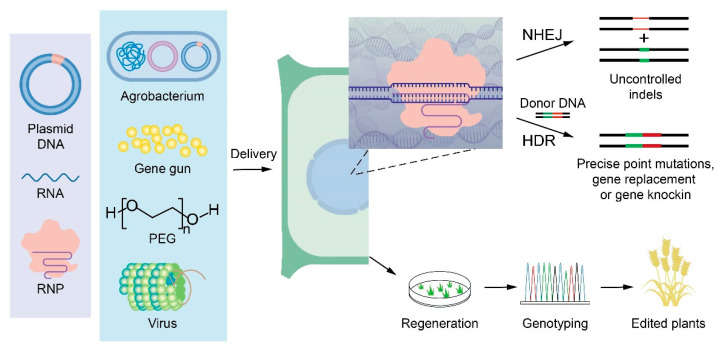
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the major steps in plant genome editing. DNA, RNA-encoding CRISPR/Cas reagents, or RNPs (composed of Cas9 and an in vitro-transcribed sgRNA) can be delivered into plant cells using Agrobacterium cells, a gene gun, polyethyleneglycol, or viruses. In the nucleus, the CRISPR/Cas reagent creates site-specific DSBs, which may be repaired through the NHEJ or HDR pathways. NHEJ generates uncontrolled, but predictable indels. In the presence of a donor template, breaks may be repaired through HDR, generating precise modifications. Gene-edited plants are identified from among the regenerated plants through genotyping.