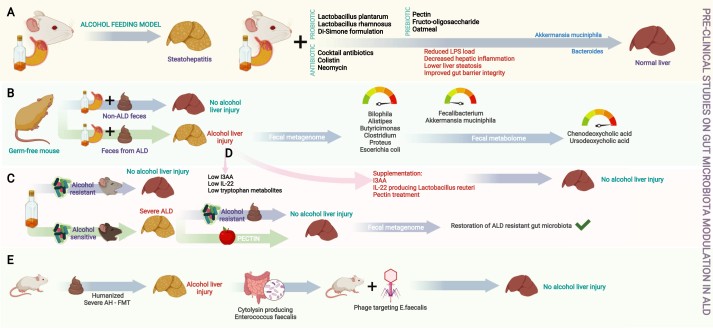
Figure 2.
Infographic summary of preclinical studies of gut microbial (GM) modulation in ALD. Various studies on probiotics, prebiotics and antimicrobial cocktails have shown that GM modulation leads to downregulation of inflammatory pathways, improvement in gut barrier integrity and thus reduction in liver injury (A); studies on germ-free mice have shown that alcohol-associated hepatitis is transferable and is associated with specific changes in the intestinal bile acid pool driven by modification of bacterial communities (B); restoration of beneficial bacterial communities was possible via prebiotic treatment (C); and supplementation of specific metabolites or beneficial metabolite producing groups of bacteria ameliorated liver injury in ALD models (D), and phage targeting of cytolysin producing Enterococcus fecalis in severe ALD improved liver injury (E). ALD—alcohol associated liver disease, FMT—fecal microbiota transplantation, I3AA—indole-3 acetic acid, IL—interleukin, LPS—lipopolysaccharide.