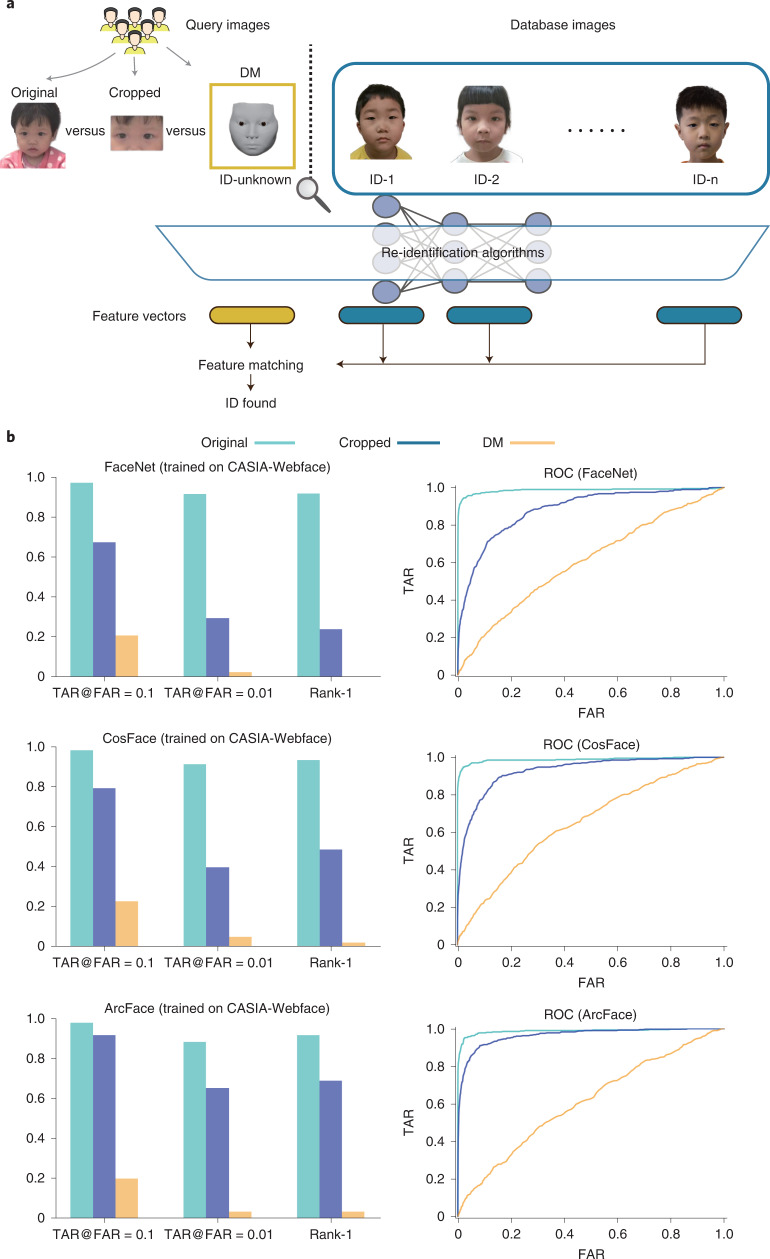
Fig. 6. Validation of the DM using AI-powered re-identification algorithms.
a, Study workflow. The re-identification algorithms were used to find the ID of the patient from a database of 405 patients when given the original image, a cropped image or the DM-reconstructed image of a patient as a query image. b, Performance of the three re-identification algorithms tested, as assessed by TAR@FAR = 0.1, TAR@FAR = 0.01, Rank-1 (left) and ROC curves (right). The re-identification algorithms were trained on the CASIA-Webface dataset. TAR@FAR = X indicates the TAR when the FAR equals X. Rank-1 is the probability that the similarity score of the same identity ranks first among all the identities. Lower values of TAR@FAR = 0.1, TAR@FAR = 0.01 and Rank-1 indicate weaker performance of the re-identification algorithm and better performance of the privacy protection technology. TAR = TP/(TP + FN); FAR = FP/(FP + TN). TP, true positive; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; FN, false negative.