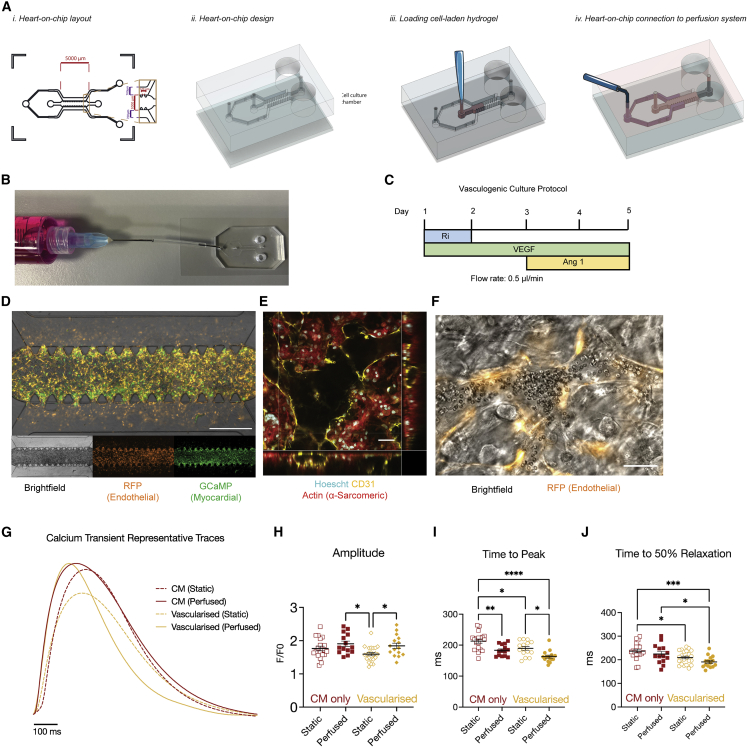
Figure 3.
Generation of perfusable myocardial microvasculature via microfluidic and vasculogenic culture
(A) Schematic of heart-on-a-chip (i) layout, (ii) design, (iii) cell seeding, and (iv) connection to perfusion.
(B) Representative image of microfluidic chip connected to syringe for perfusion (tubing shortened for display).
(C) Vasculogenic culture protocol. Ri, Rho/ROCK inhibitor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; Ang-1, angiopoietin 1.
(D) Representative image of cellular distribution in microfluidic chips (EC = RFP-HUVEC). Scale bar: 1 mm.
(E) Confocal z stack demonstrating myocardial microvasculature with open lumen. White asterisk represents open luminal space (EC = hCMVEC). Scale bar: 50 μm (Video S3).
(F) Live-cell image of perfused erythrocyte in myocardial microvasculature lumen (EC = RFP-HUVEC). Scale bar: 50 μm (Video S4).
(G) Representative Ca2+ transient traces in heart on a chip under vascularized and/or perfused conditions.
(H–J) Quantification of Ca2+ transient (H) amplitude and (I and J) kinetics under vascularized and perfused conditions.
Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Each datapoint represents 1 chip, containing average of 3 regions of interest (ROIs; 5–15 cells), 3 beats/ROI.