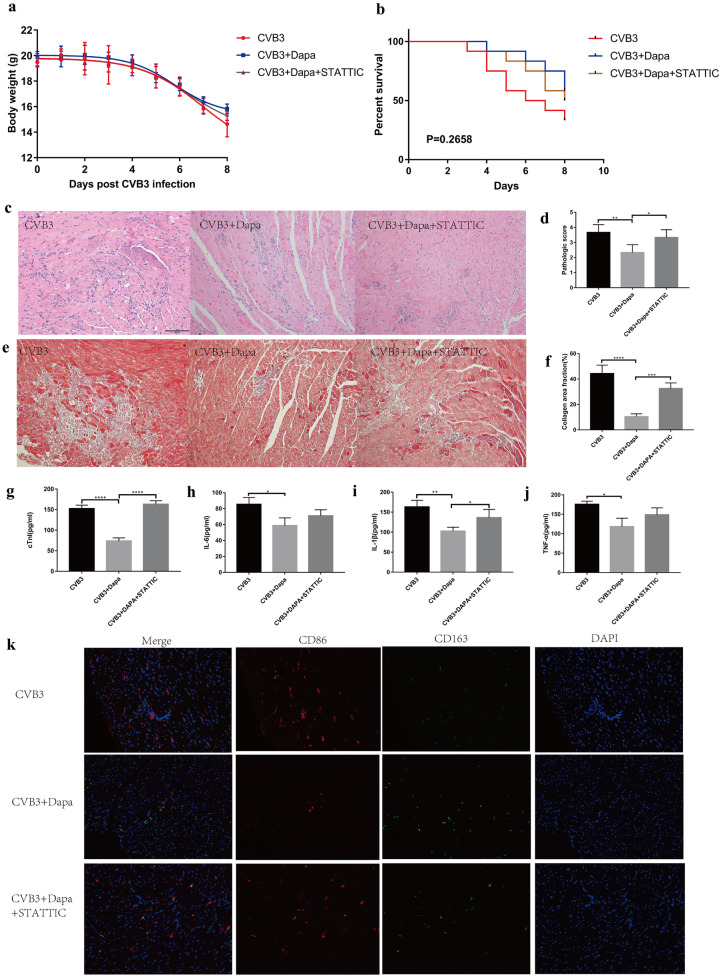
Fig. 3.
STATTIC eliminates the therapeutic effect of dapagliflozin in VMC. a Body weight change and b survival rate of mice from day 0 to day 8. c Hematoxylin–eosin staining to observe the inflammatory response to myocarditis. Red-stained area shows myocardial tissue, blue staining shows inflammatory cell infiltration (magnification: × 200, scale bar: 100 µm). d The severity of myocarditis was scored using standard 0–4 grading scale. e Masson staining to observe the inflammatory response to myocarditis. Myocardial cells were stained red and collagenous fibers were stained blue (magnification: × 200, scale bar: 100 µm). f Collagen area fraction (collagen area/field area × 100%) was calculated by the Image-Pro Plus analysis system. g Serum myocardial injury markers cardiac troponin I (CTnI) were measured by ELISA. h, i, j Serum inflammation markers IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were measured by ELISA. k Immunofluorescent double staining of myocardial tissue with antibodies to CD68 and CD163. Red indicates CD68 (one marker for M1), green CD163 (one marker for M2), and blue DAPI-stained cellular nuclei. Data were shown as mean ± SD (CVB3, CVB3-infected mice treated with 60% propylene glycol; CVB3 + Dapa, CVB3-infected mice treated with dapagliflozin; CVB3 + Dapa + STATTIC, CVB3-infected mice treated with dapagliflozin and STATTIC, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).