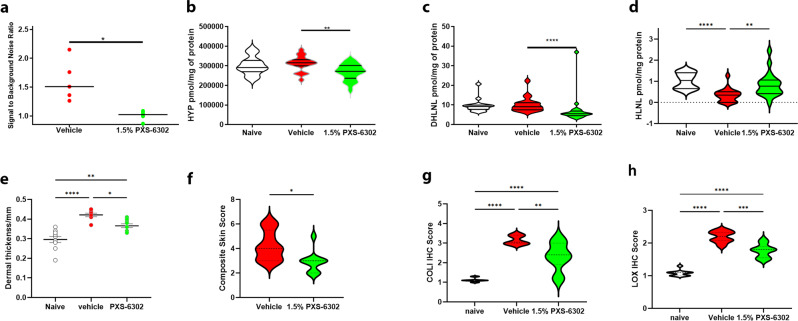
Fig. 6. Topical PXS-6302 is effective in reducing bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis.
Topical treatment with 1.5% PXS-6302 cream significantly inhibited LOX activity (a (p = 0.001)), reduced hydroxyproline (b (p = 0.048)) and immature DHLNL (c (p < 0.0001)) and HLNL (d (p < 0.0001)) crosslinks in the skin and reduced fibrosis as assessed by dermal thickness (e (p = 0.0139 and 0.0013 vehicle and naïve vs PXS-6302 treated respectively)) and Composite skin scores (f (p = 0.0114)). Immunohistochemistry also showed reduced Col I (g (p = 0.0006)) and LOX (h (p < 0.0001)) positive staining in 1.5% PXS-6302 treated tissue sections. Naïve animals were not exposed to bleomycin, whilst vehicle and PXS-6302 groups were treated with bleomycin to induce fibrosis (n = 9–10 per group). Statistical analysis was performed with two-tailed Mann–Whitney test or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s method for multiple comparisons. p values are <0.05 (*), <0.01 (**), <0.001 (***) and <0.0001 (****). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.