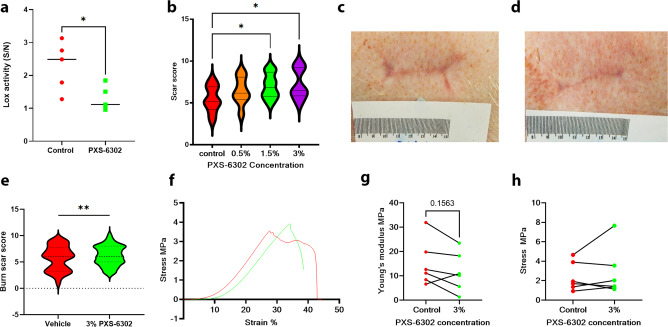
Fig. 8. Topical treatment with PXS-6302 inhibits LOX, reduces crosslinking and improves scar appearance in porcine models of excisional and burn injury.
LOX activity is significantly inhibited in porcine scar 24 h after final daily PXS-6302 application (total duration of application once daily for 10 weeks (a (p = 0.0292))). b Independently scored scars on a scale of 1–10 (poor to good scar) by plastic surgeons blinded to treatment show significantly higher scores for the 3% PXS-6302 treated scars in excision injury model (p = 0.0028, 0.0334 3% treatment vs control and 0.5% treatment respectively). Images of vehicle (c) and 3% PXS-6302 (d) treated scar after excision (e) Scars after burn injury were also significantly improved compared to placebo-treated control when scored independently by plastic surgeons blinded to the treatment group. (f (p = 0.008)) Stress–strain curves of treated (green) and control (red) scars were similar, with a reduction in Young’s modulus in 5/6 treated scars compared to matched controls (g, h) and no difference in tensile strength between the two groups (n = 10 excision wounds each treatment group, n = 12 burn injuries in treated and control groups). Statistical analysis was performed with paired Mann–Whitney test or repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s method for multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.