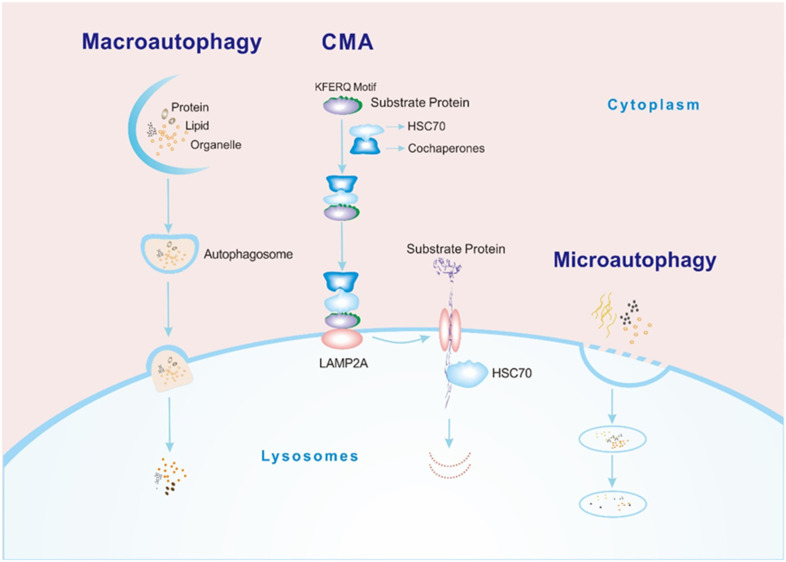
Figure 1.
Processes of 3 types of autophagy. Macroautophagy: cargos (such as proteins, lipids, and organelles) combine with vesicles in the cytoplasm to form an autophagosome. The autophagosome fuses with the lysosomal membrane, and then the cargos enter the lysosomal cavity and are degraded by hydrolase. CMA: (1) The HSC70-cochaperone complex recognizes the KFERQ sequence of the substrate protein. (2) The substrate binds to the cytoplasmic segment of LAMP2A on the lysosomal membrane. (3) The LAMP2A monomer polymerizes to form a transport complex, and the substrate adopts an extended conformation and passes through the lysosomal membrane into the lysosomal cavity with the assistance of HSC70 in the lysosomal cavity. (4) The substrate is degraded. Microautophagy: the lysosomal membrane directly invaginates to form vesicles, and the cargos are enveloped within the lysosomal cavity for degradation.
Abbreviations: CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy; HSC70, heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein; LAMP2A, lysosome-associated membrane protein type 2A.