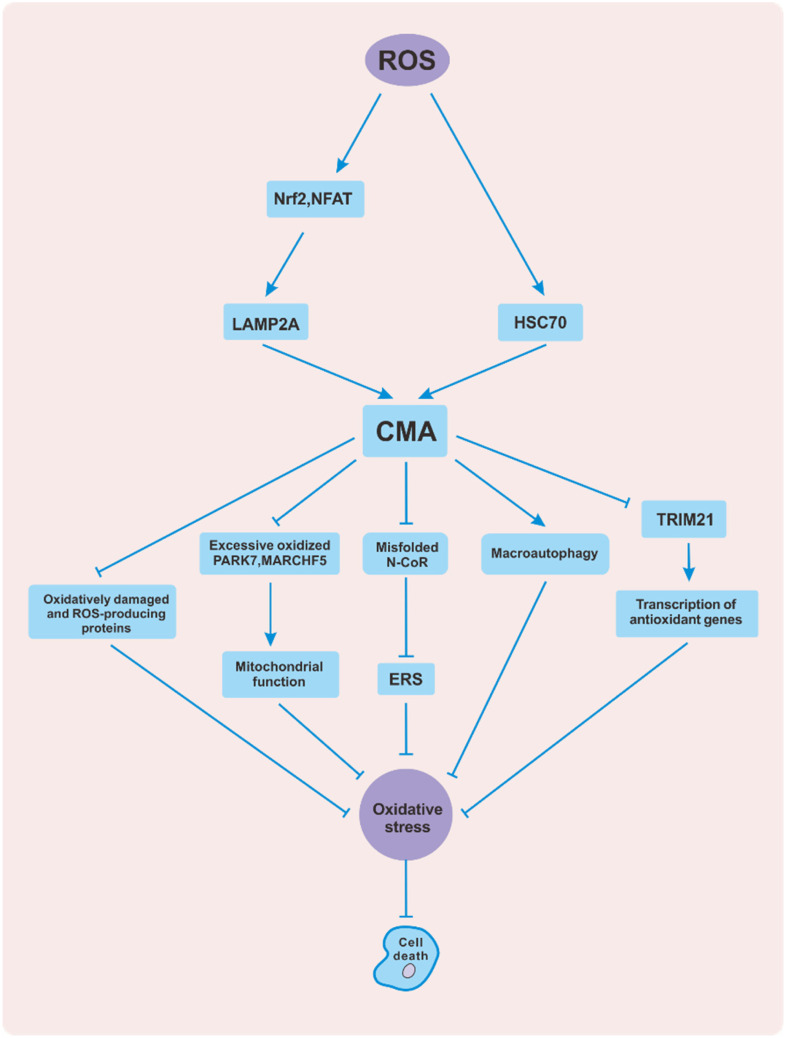
Figure 2.
Interaction between ROS and CMA. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) activate CMA by promoting the expression of LAMP2A and HSC70. In contrast, CMA defends against oxidative stress in several ways to protect cells from apoptosis. For example, CMA directly scavenges oxidatively damaged and ROS-producing proteins. In addition, CMA indirectly regulates mitochondrial function, ERS, the macroautophagy pathway, and antioxidant gene transcription. Abbreviations: ROS, reactive oxygen species; CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy; HSC70, heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein; LAMP2A, lysosome-associated membrane protein type 2A; ERS, endoplasmic reticulum stress; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PARK7, parkinsonism associated deglycase; MARCHF5, membrane-associated ring-CH-type finger 5; N-CoR, nuclear receptor corepressor; TRIM21, tripartite motif containing 21.